China’s AI Leap: Talent, Innovation and Global Tech Impact
In early 2025, an unknown Chinese startup named DeepSeek launched DeepSeek-R1, an open-source large language model (LLM) that made global headlines. The model not only rivaled established LLMs such as GPT-4, Llama 3.1, and Claude in performance but achieved this at significantly lower costs and with reduced training data requirements.
The unexpected breakthrough ignited an intense debate: Was this a fleeting success, or had China truly asserted its place as a formidable competitor in the global AI landscape?
DeepSeek's achievement wasn't an isolated event. Rather, it reflected years of groundwork that has shaped China's AI ecosystem—carefully fostered through academic research, talent cultivation, innovation under constraints, and fierce internal competition.
How is China orchestrating this transformation, and what does it mean for global businesses and investors?
Strategic Investments in Research and Innovation
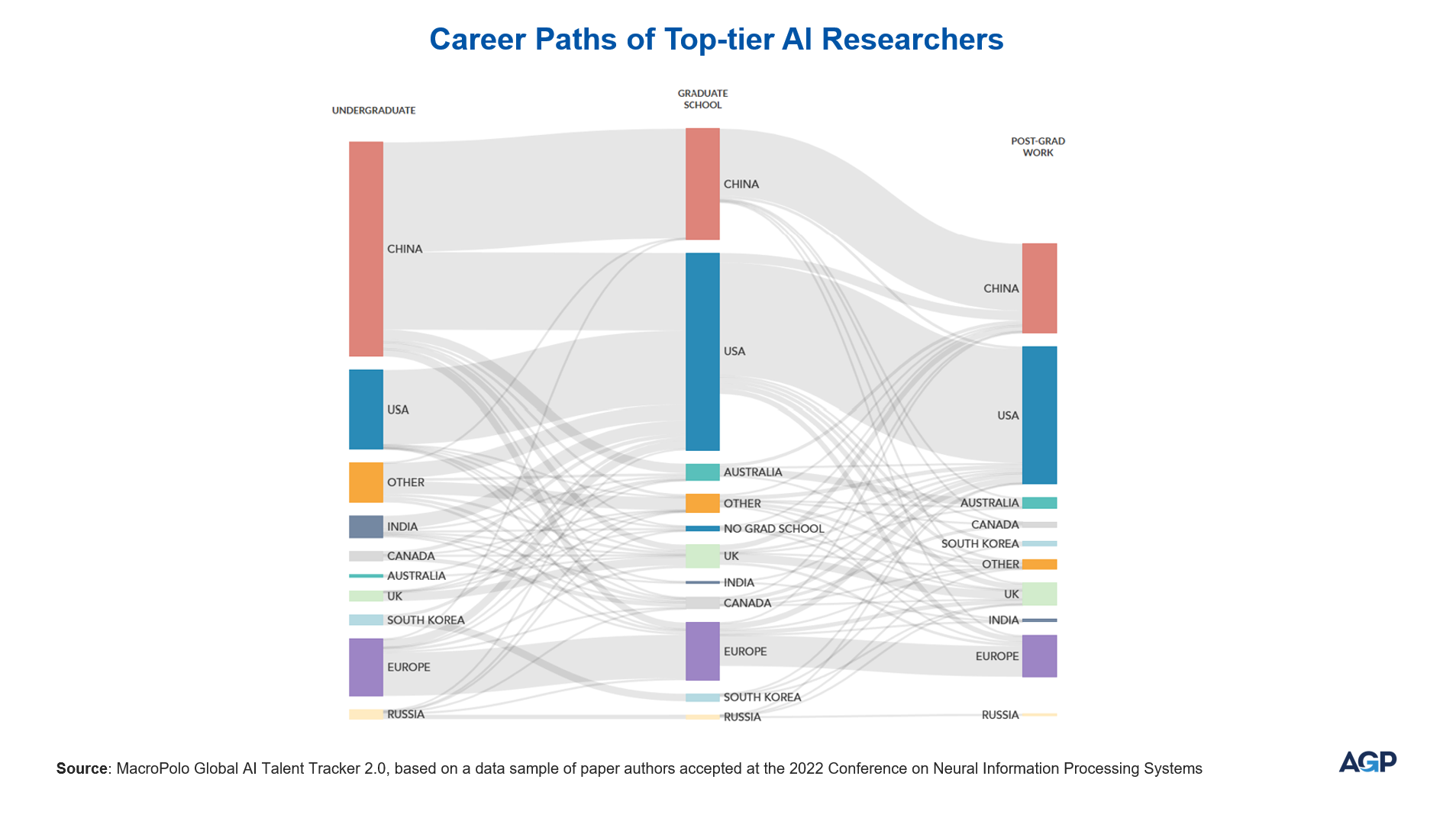
China's pursuit of AI leadership has been built upon systematic, long-term investments in both academic research and applied innovation. Over recent years, the country has significantly expanded its domestic research capabilities, clearly demonstrated by its growing prominence in global AI research. Between 2019 and 2023, China's share of the world's leading AI researchers surged from 11% to 20%, according to MacroPolo’s Global AI Talent Tracker. This increase in top-tier talent has driven a greater number of Chinese professionals into careers within China's rapidly evolving AI industry.
Since 2018, more than 500 Chinese universities and colleges have introduced AI-related majors, following the release of Beijing’s "New Generation Artificial Intelligence Development Plan," a comprehensive strategy aiming to establish China as a global AI leader.
Today, according to the World Intellectual Property Organization, China has surpassed the U.S. in AI research publications and patent filings. Between 2014 and 2023, China's AI patent filings were six times higher than those of the U.S. However, despite this prolific output, Chinese patents generally receive fewer citations internationally, indicating that while extensive, China's research has not yet achieved full global influence. Nevertheless, this extensive intellectual groundwork is foundational to the country's long-term competitive advantage in AI.
Developing a New Generation of AI Talent
China’s focus on talent cultivation is another critical factor driving its ascent in AI. Major Chinese tech companies have actively developed thousands of skilled programmers and data scientists across sectors like e-commerce, gaming, and digital marketing, contributing to a robust domestic talent pipeline.
Recent research further underscores China's emergence as a global leader in AI talent production, with the country now accounting for nearly half of the world's top AI researchers. In comparison, just 18% of the leading global researchers completed their undergraduate education in the U.S., according to the MacroPolo study. Only three years ago, China contributed roughly one-third of the global leading talent pool, while the proportion from the U.S. remained largely unchanged.
This shift in talent dynamics has been developing steadily over the past decade. Throughout much of the 2010s, the U.S. attracted a significant number of China's top students to complete doctoral studies, many of whom stayed to work in the U.S. afterward. The MacroPolo research, however, reveals a reversal in this trend, with an increasing number of Chinese researchers now choosing to build their careers within China’s own vibrant AI ecosystem.
The Obstacle is the Way
In response to escalating technology restrictions, particularly the U.S. export controls on advanced semiconductors initiated in 2022, Chinese firms have intensified efforts to bolster their domestic capabilities.
Advancements in domestic chip development. Huawei has made significant strides in AI chip production. By early 2025, the company improved its production yields of advanced AI chips to nearly 40%, a notable increase from 20% the previous year. This progress supports China's ambition to develop its semiconductor technology amid U.S. export restrictions. Huawei's Ascend 910C processors, which outperform the previous 910B model, have become profitable, with plans to increase production to 100,000 units within the year. Alongside Huawei, other companies such as SenseTime and Xiaomi are heavily investing in chip development.
Open-source AI Models as a strategic response. In addition to hardware advancements, Chinese tech companies have embraced open-source AI models to circumvent technological limitations. Major firms, including Alibaba, Baidu, and Tencent, have rapidly released sophisticated AI models that are free to download, modify, and integrate. This approach allows China to bypass U.S. sanctions, decentralize AI development, and tap into global talent, thereby promoting continuous improvement of their models. By making AI widely accessible, China challenges the current monetization strategies of U.S. AI companies, which maintain exclusivity through paid subscriptions and enterprise deals.
Leveraging older-generation chips. To further mitigate the impact of export controls, Chinese AI startups have focused on developing models optimized for older-generation chips. DeepSeek, mentioned earlier, has developed large language models (LLMs) capable of running efficiently on less advanced hardware. This strategy enables the deployment of competitive AI solutions without relying on cutting-edge semiconductors, effectively sidestepping restrictions on high-end chip imports.
Fierce Internal Competition
The growth of China's AI industry has been remarkable, with over 237,000 new AI-related companies established in the first half of 2024 alone, bringing the total to approximately 1.67 million, according to corporate data provider Qichacha.
However, this rapid expansion is not without challenges. A recent report by Commercial Times, citing Chinese media TMTPost, highlights a significant mortality rate among these startups: nearly 80,000 AI companies have either shut down or suspended operations within the past 600 days. This indicates that despite vigorous growth, the competitive landscape is fierce, and sustainability remains a critical concern for new entrants in China's AI ecosystem.
Financial Government Support
China’s development model, strategically encouraged by government policies, has proven effective across various emerging sectors, including electric vehicles, solar, and wind energy.
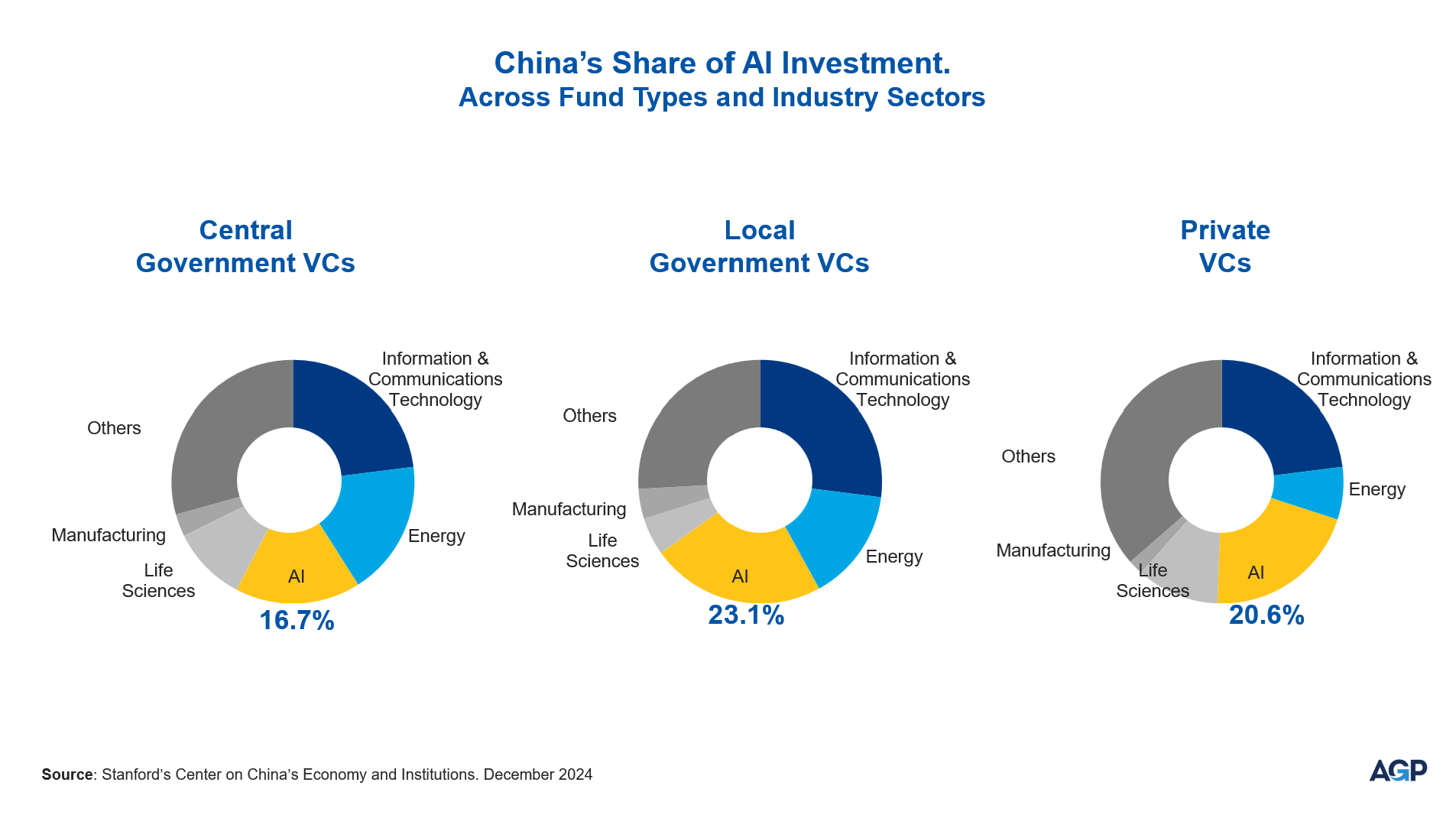
Between 2013 and 2024, China’s central and local government venture funds injected over US$912 billion into strategic industries, with AI-focused companies receiving nearly a quarter of this investment, according to a report by Stanford’s Center on China’s Economy and Institutions. Between 2000 and 2023, 4,115 AI firms received investments from both government and private VCs; 71% of these were funded first by public VC funds. In China’s low-information business environment, government VC funds—with access to exclusive information—may act as signals for private VCs to follow.
Final Considerations
China's accelerated advancements in AI represent both significant opportunities and notable challenges for global innovation leaders, China-based executives, and senior strategists at multinational corporations.
China's comprehensive investments in AI research, talent cultivation, and strategic support highlight the country's clear and long-term vision of achieving global AI leadership. Multinational companies must understand and strategically leverage China's growing domestic capabilities, considering further partnerships with local academic institutions and research hubs that have rapidly matured in recent years.
The rise of domestic AI talent and a growing preference among Chinese AI researchers to remain in China rather than moving abroad signals a significant shift. Global corporations need agile talent acquisition and retention strategies, carefully balancing competitive compensation with robust intellectual property protection measures, to succeed in China’s increasingly competitive labor market.
Related Insights.