Innovating in China. 2024 Strategic Landscape for Multinationals
China’s rise as a global innovation power results from well-designed strategies that combine its engineering talent, strong policy support, and broad market reach. Multinational companies (MNCs) seeking growth in this dynamic landscape face unique challenges and strategic decisions.
Based on findings from the 2024 Innovating in China benchmarking study by the Asia Growth Exchange initiative, this Insight addresses key questions related to innovation investment, structuring, and technology adoption in China, emphasizing why the country is crucial for forward-thinking MNCs.
The Significance of Innovating in China
China’s position in global innovation is grounded in its strong scientific and engineering capabilities, an R&D-friendly ecosystem, and strategic focus on future-defining industries.
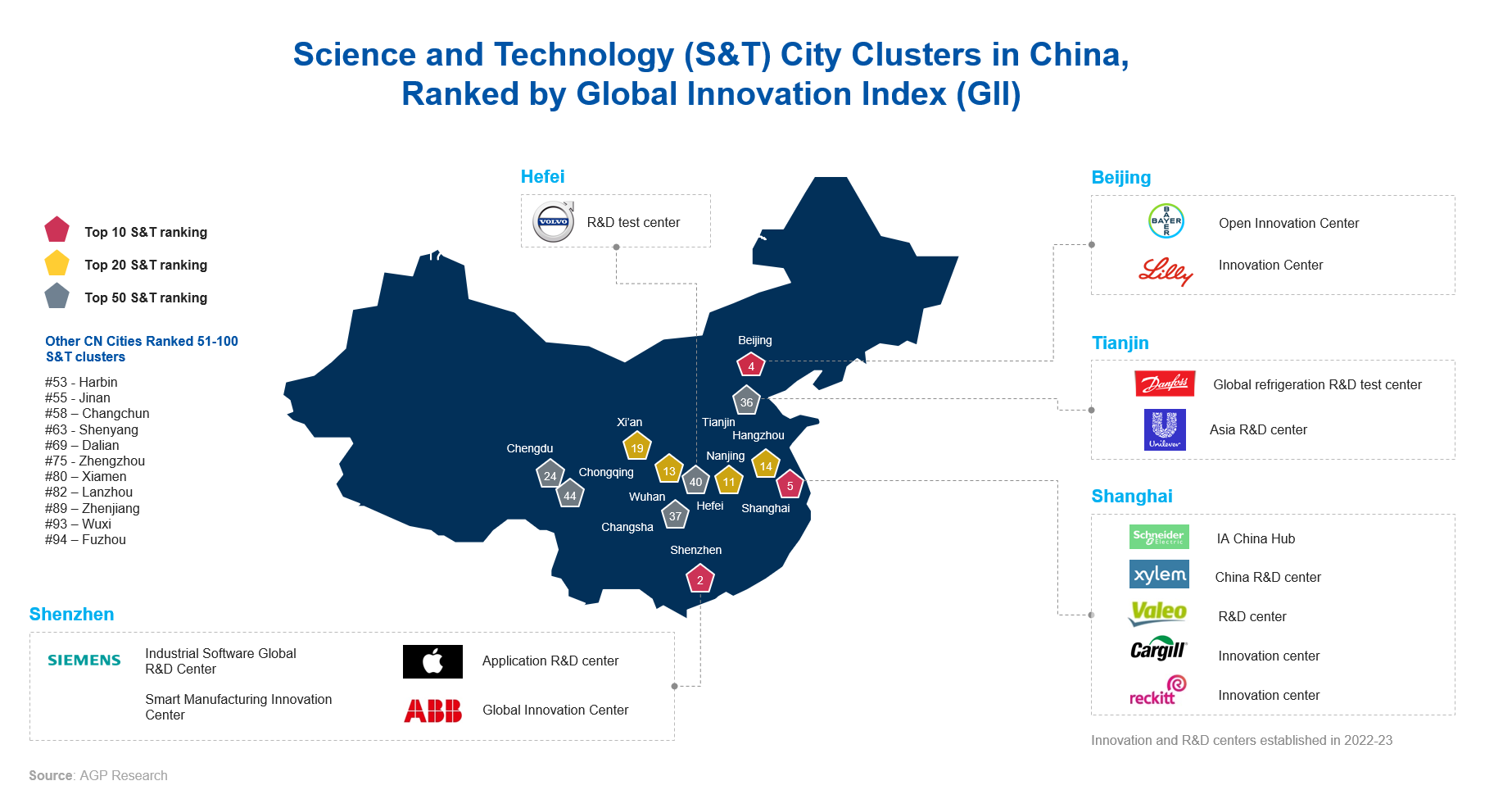
China is home to three top 10 and 12 of the top 50 science and technology city clusters ranked by the Global Innovation Index (GII). These cities form a growing cluster of innovation and R&D centers.
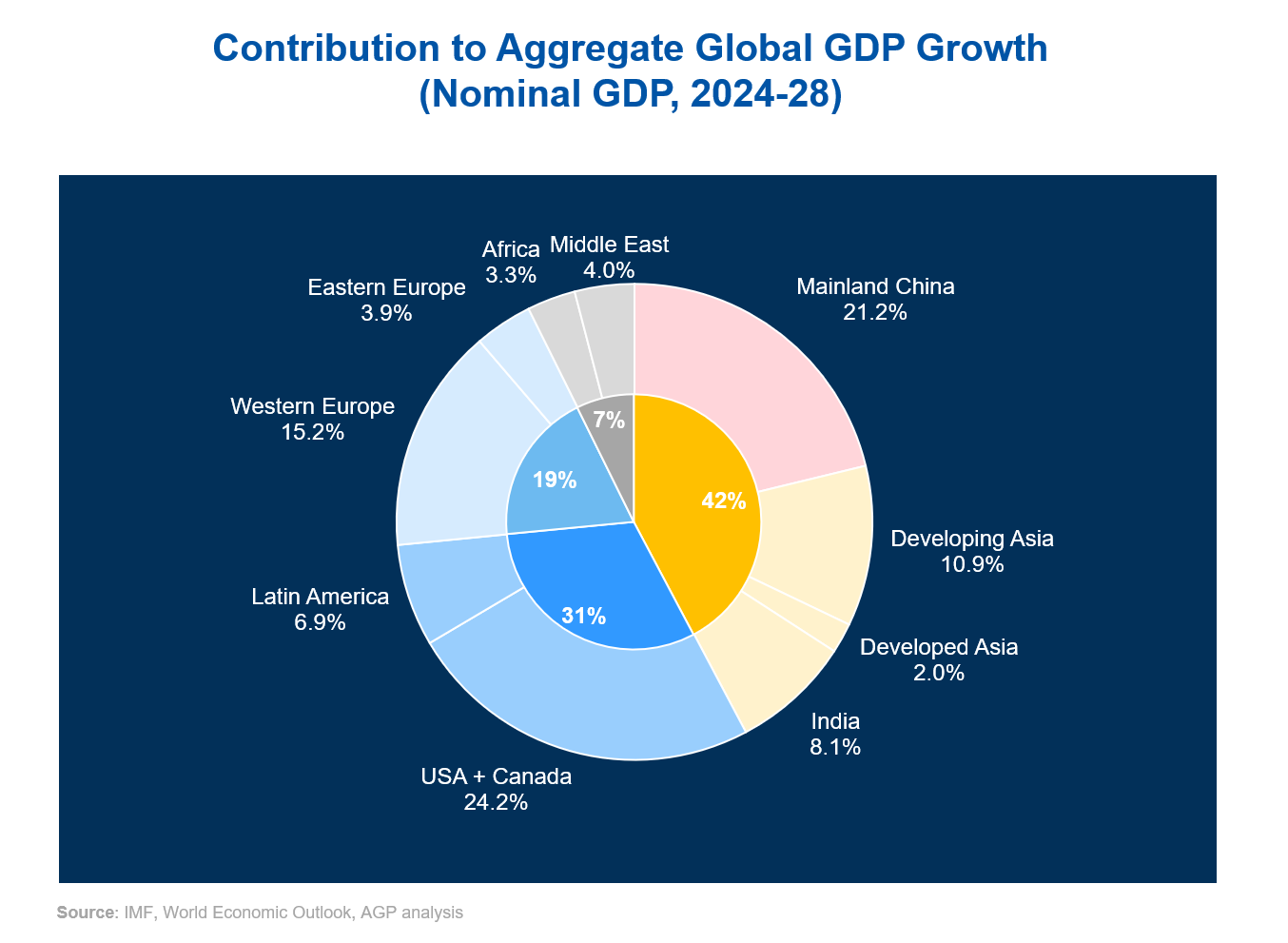
China alone will contribute 21% of global GDP growth during the five-year period from 2024 to 2028. With its plans to establish itself as a global leader in innovation by 2028, China invests heavily in core technologies and creates platforms to bring new ideas to market. The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has identified priority sectors, such as AI, advanced materials, and next-gen manufacturing, for funding and policy emphasis.
For MNCs, these developments highlight the importance of aligning their strategies with the "China for China" and "China for Global" models. The latter underscores China's role not just as a significant market but also as an R&D base that contributes to global operations. This shift away from the traditional “Global for China” approach demonstrates a growing recognition of China’s potential to drive global product strategies.
Investment Trends in China’s Innovation Ecosystem
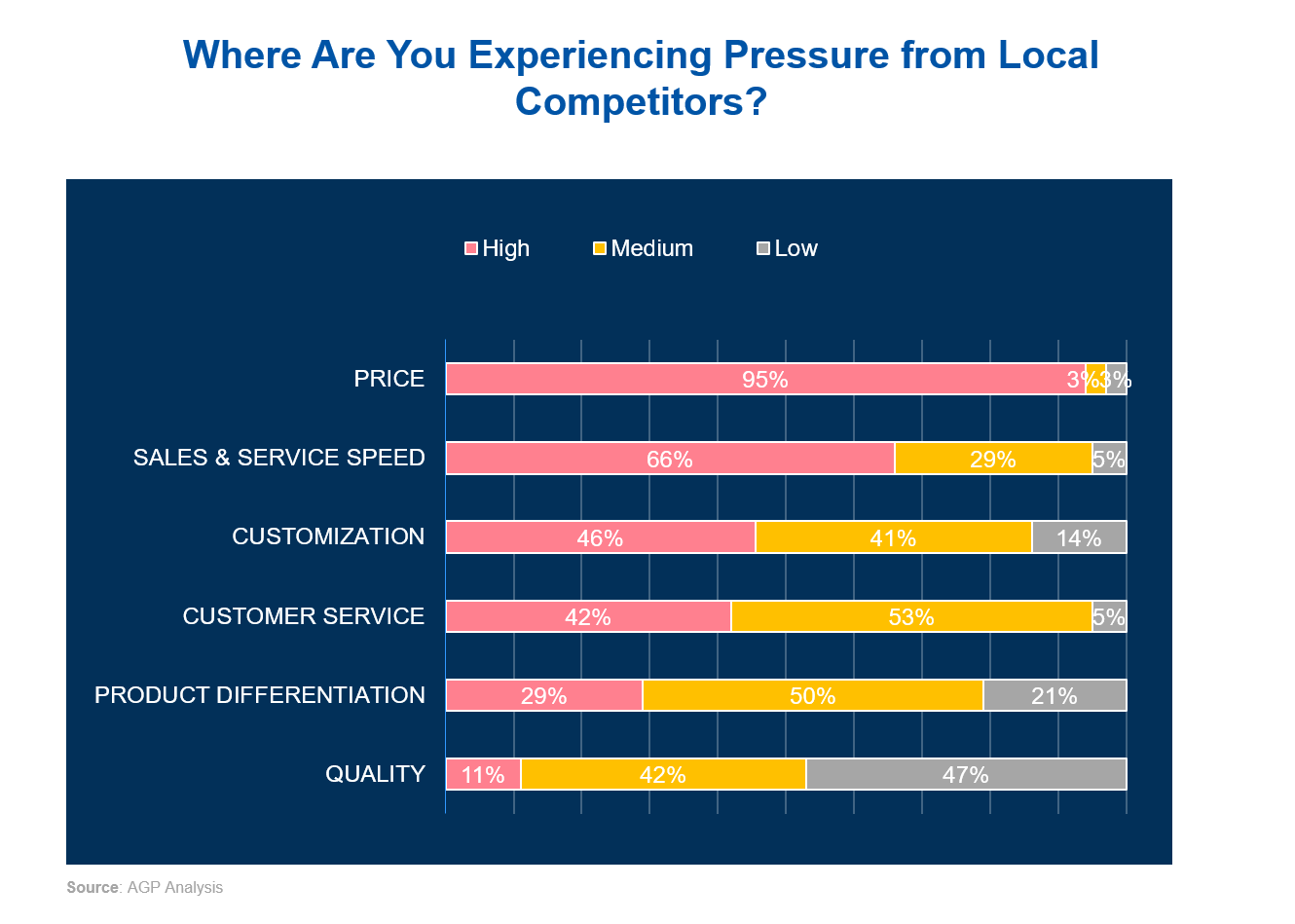
Competitive pressure from local players is fierce, with the greatest challenges in pricing and sales/service speed. Only 3% and 5% of multinational companies, respectively, feel that their current operations are strongly competitive in these areas.
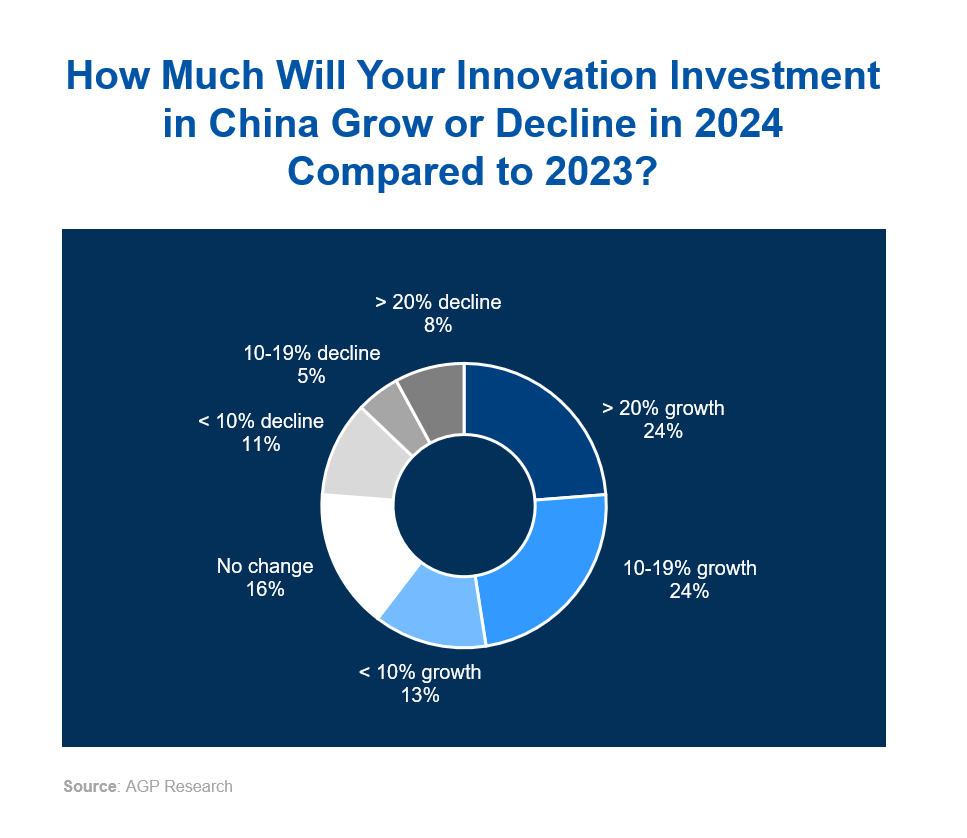
Despite competitive pressure and overall reductions in Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) into China, MNCs’ innovation budgets have remained robust. In 2024, 61% of surveyed companies reported an increase in innovation spending, signaling confidence in China’s technological landscape and growth potential. This commitment goes beyond local presence and reflects confidence in China’s capacity as a leader in developing and implementing advanced solutions.
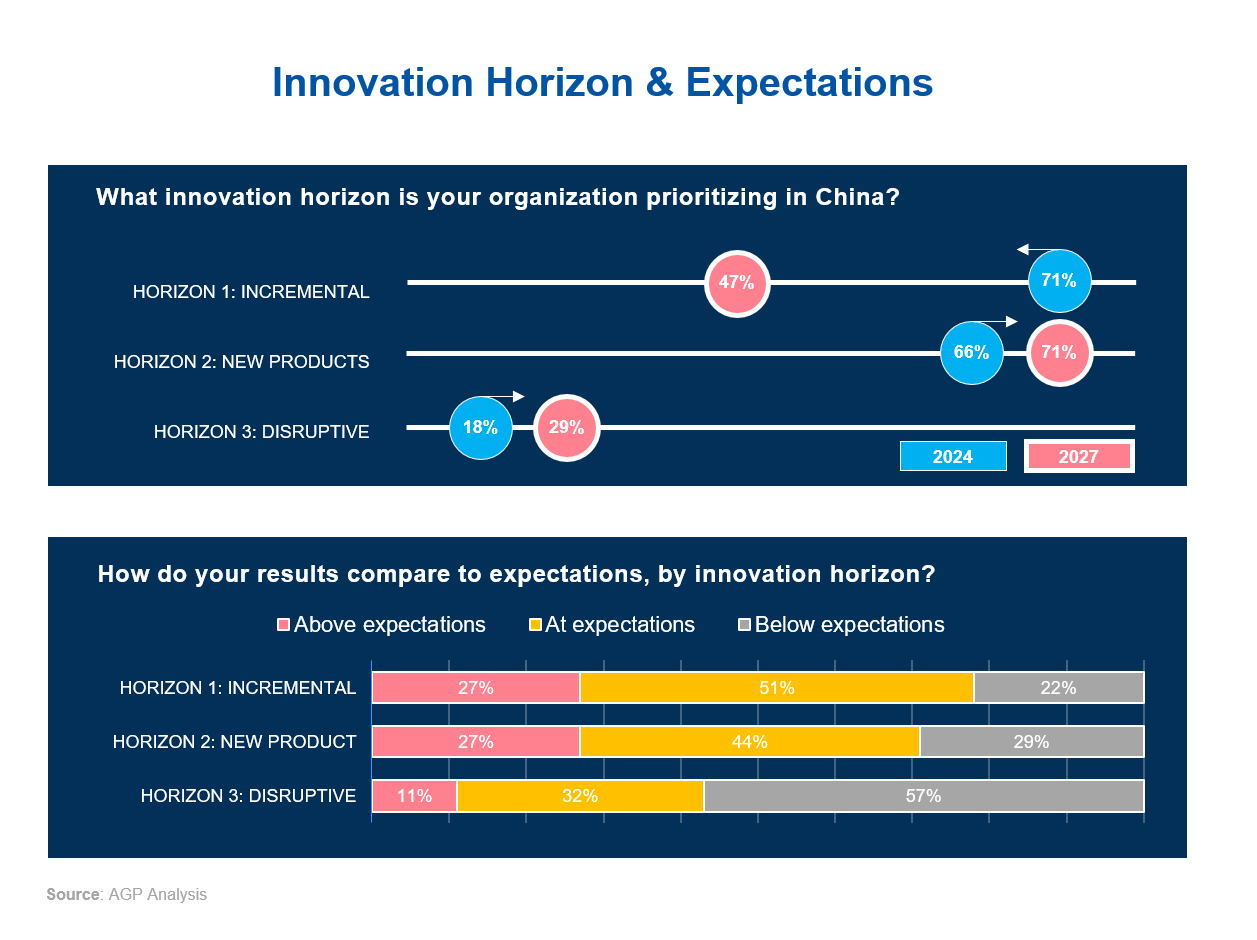
There is a noticeable trend among MNCs in China to prioritize new and disruptive innovation, as incremental innovation fails to protect market share. By 2027, the proportion of companies focusing on new product innovation is projected to grow from 66% to 71%, while those focusing on incremental innovation will decrease from 71% to 47%.
Disruptive innovation is also expected to increase in priority, with the percentage of MNCs emphasizing this type of innovation rising from 18% in 2024 to 29% in 2027, despite challenges in meeting expectations.
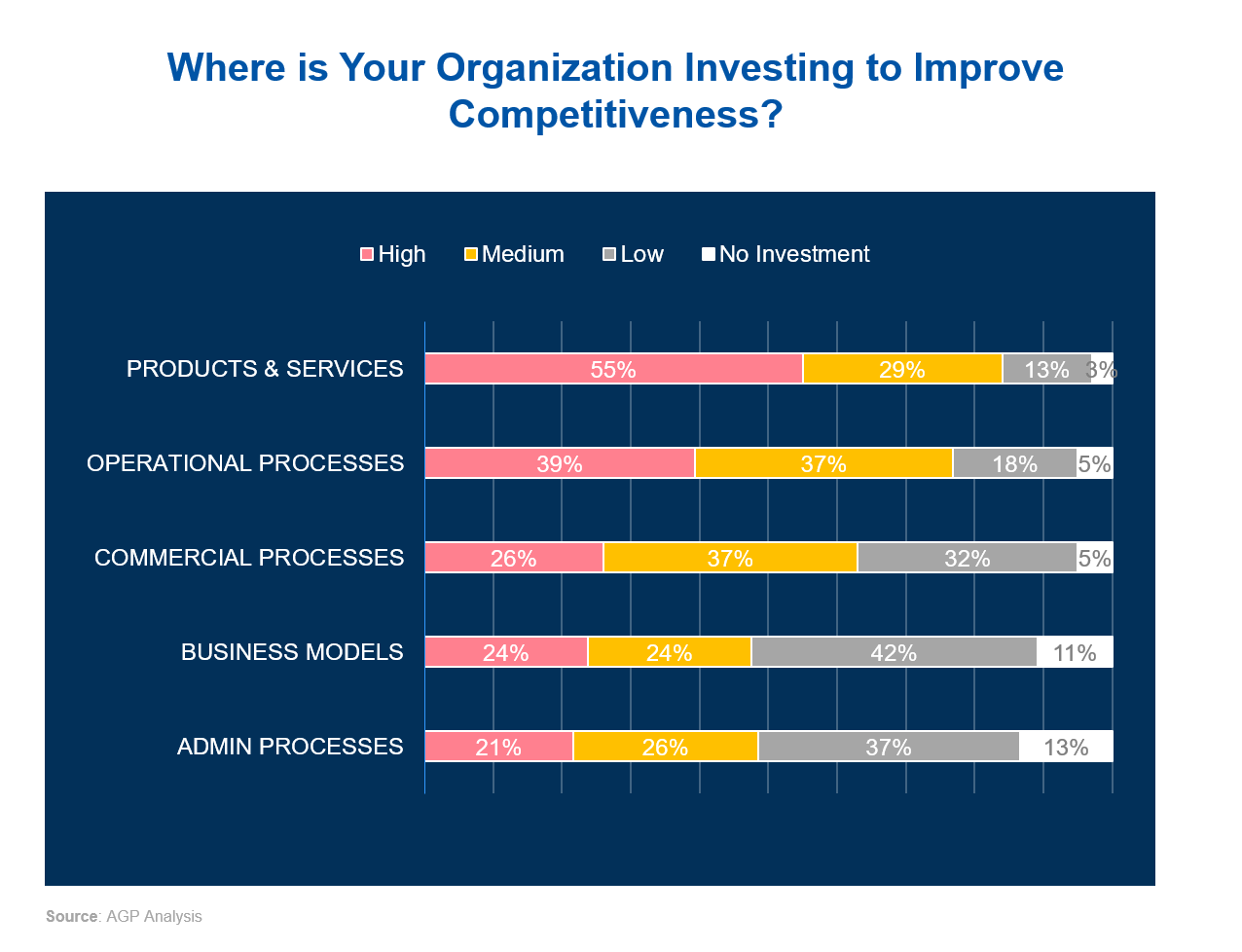
To reduce the price and sales/service speed gap, larger MNCs are investing heavily in operational and commercial process digitalization, while smaller players focus on product development and localization.
Structuring Innovation in China
Traditionally, MNCs relied on headquarters-led strategies for localizing products for China. However, this often limited adaptability and quick action.
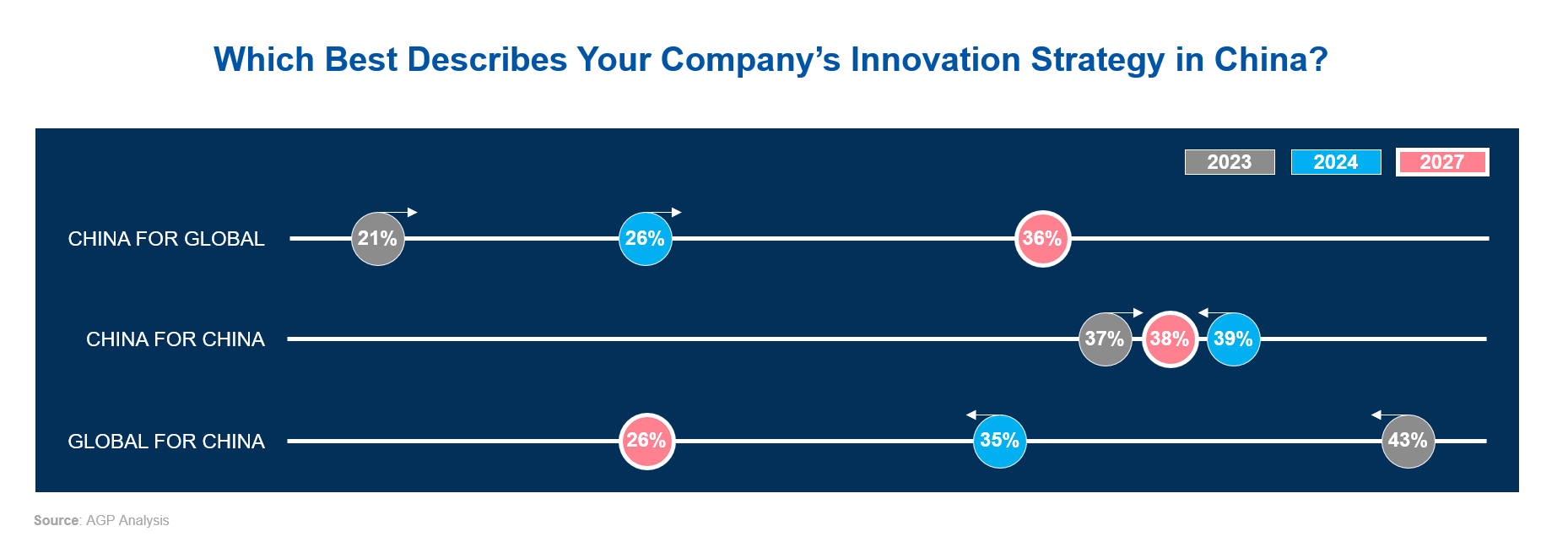
The survey results in both 2023 and 2024 indicate a strong shift away from a “Global for China” towards a mix of “China for China” and “China for Global” strategies. The proportion of companies adopting a "China for Global" strategy is expected to grow significantly, from 26% in 2024 to 36% by 2027. The percentage of companies focusing on the "China for China" approach remains steady, from 39% in 2024 and 38% by 2027. This shift reflects an understanding that China’s innovation capabilities are now strong enough to contribute effectively to global product lines. By integrating global and local teams and moving strategic product development to China, companies can leverage the country’s fast prototyping and market response abilities.
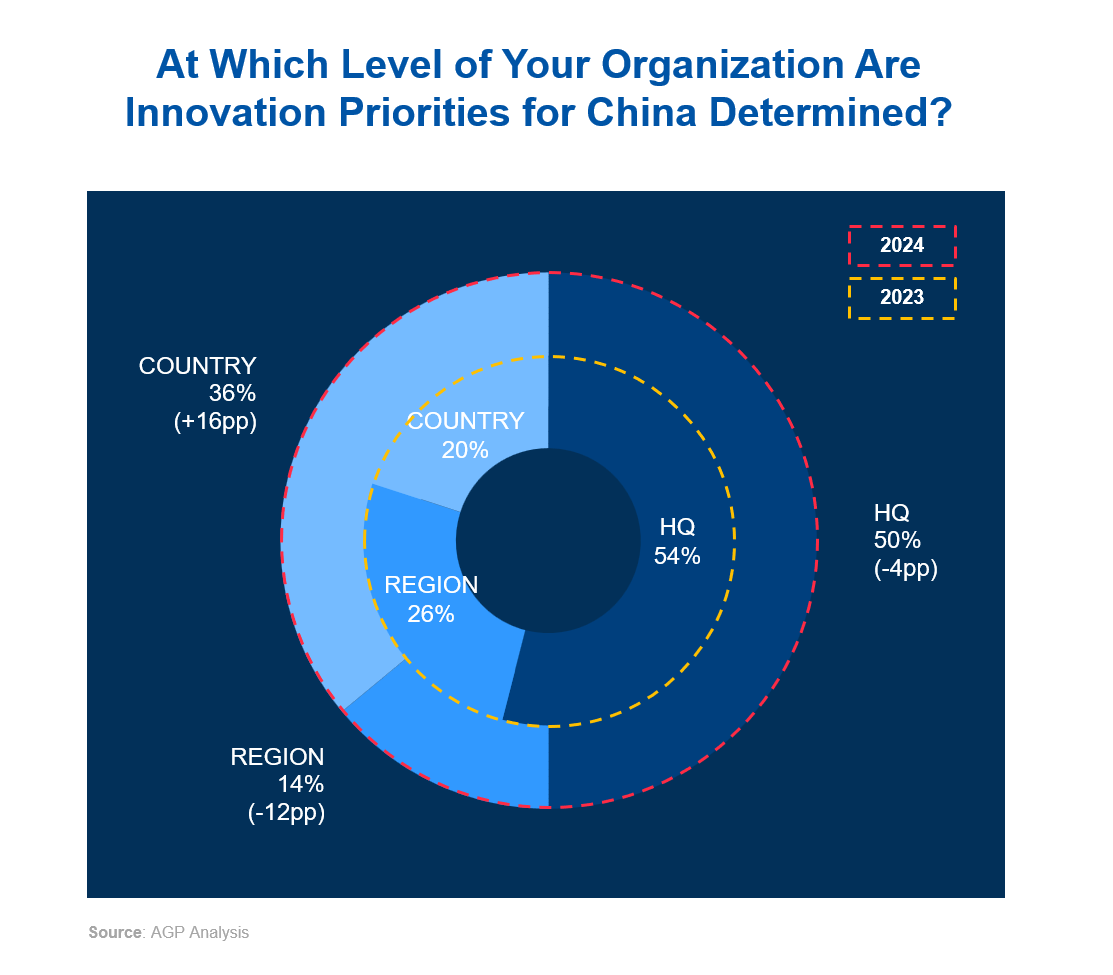
Due to the COVID-19 lockdowns in 2022, innovation decision-making significantly shifted to the regional level, with many operations managed from hubs like Singapore. However, in 2024, there is a noticeable shift back towards decision-making at the country level, indicating a return to localized control and strategic alignment.
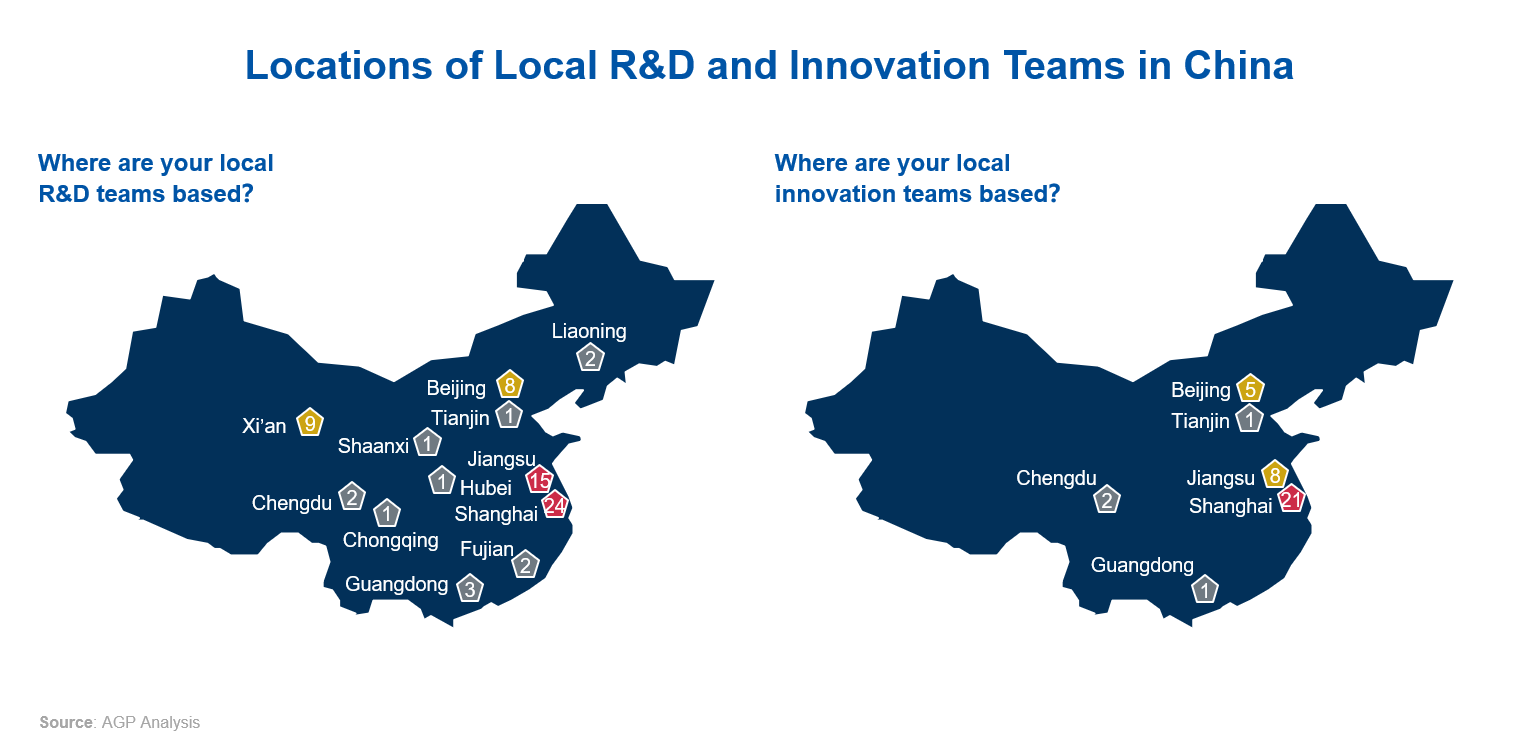
64% of MNCs’ R&D and innovation centers are concentrated in Shanghai and Jiangsu, with a further 12% clustered in Beijing. The locations of R&D teams are more geographically fragmented than innovation teams since they require a higher investment in technical talent, which is less expensive outside tier-one cities. Innovation hubs tend to be located close the business, and often require English fluency to enable communication with global.
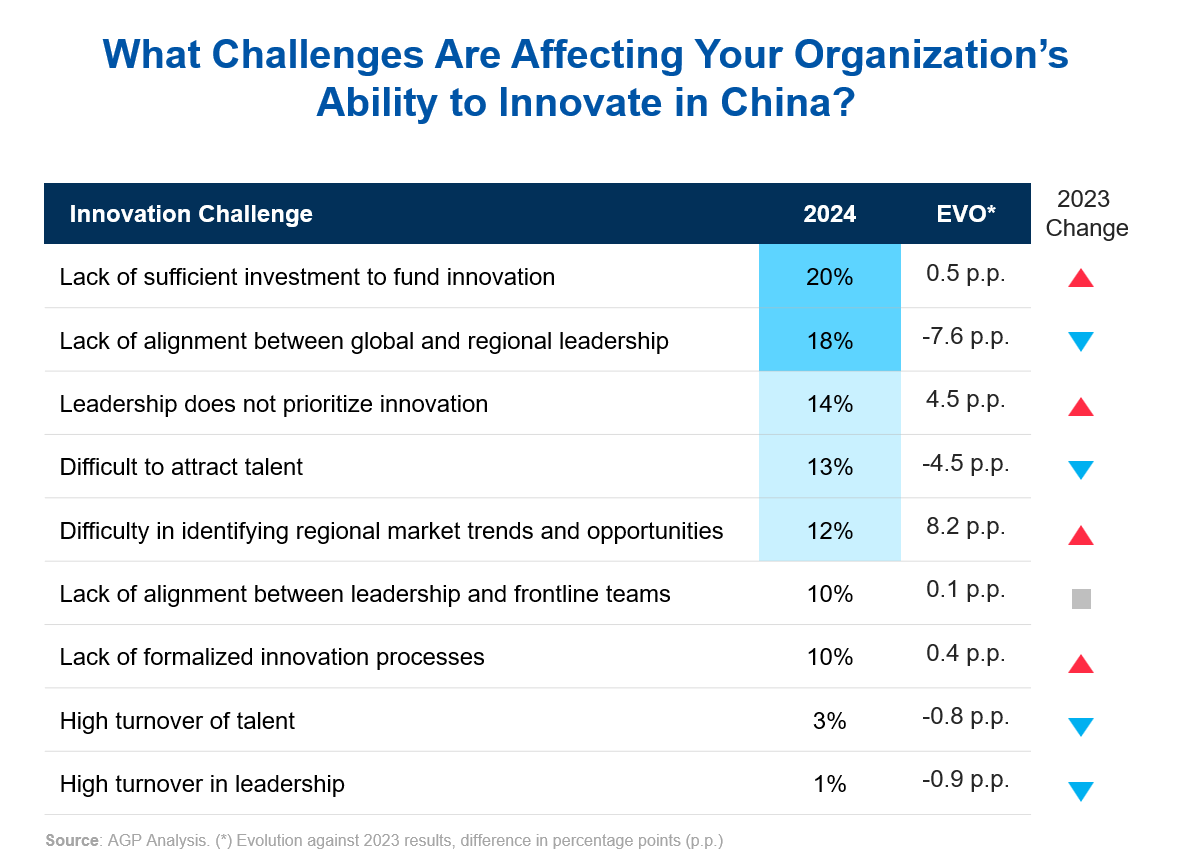
Challenges Limiting Innovation Outcomes
Although the opportunities in China are substantial, several challenges can hinder effective innovation. Financial limitations underscore the need for companies to allocate resources effectively. Insufficient funding is a significant obstacle, with 20% of MNCs citing inadequate financial resources. Additionally, while alignment between global and regional leadership has improved following the resumption of international travel, it remains a challenge for 18% of MNCs. Misalignment can create delays and weaken the impact of initiatives when local insights are not effectively integrated into decision-making.
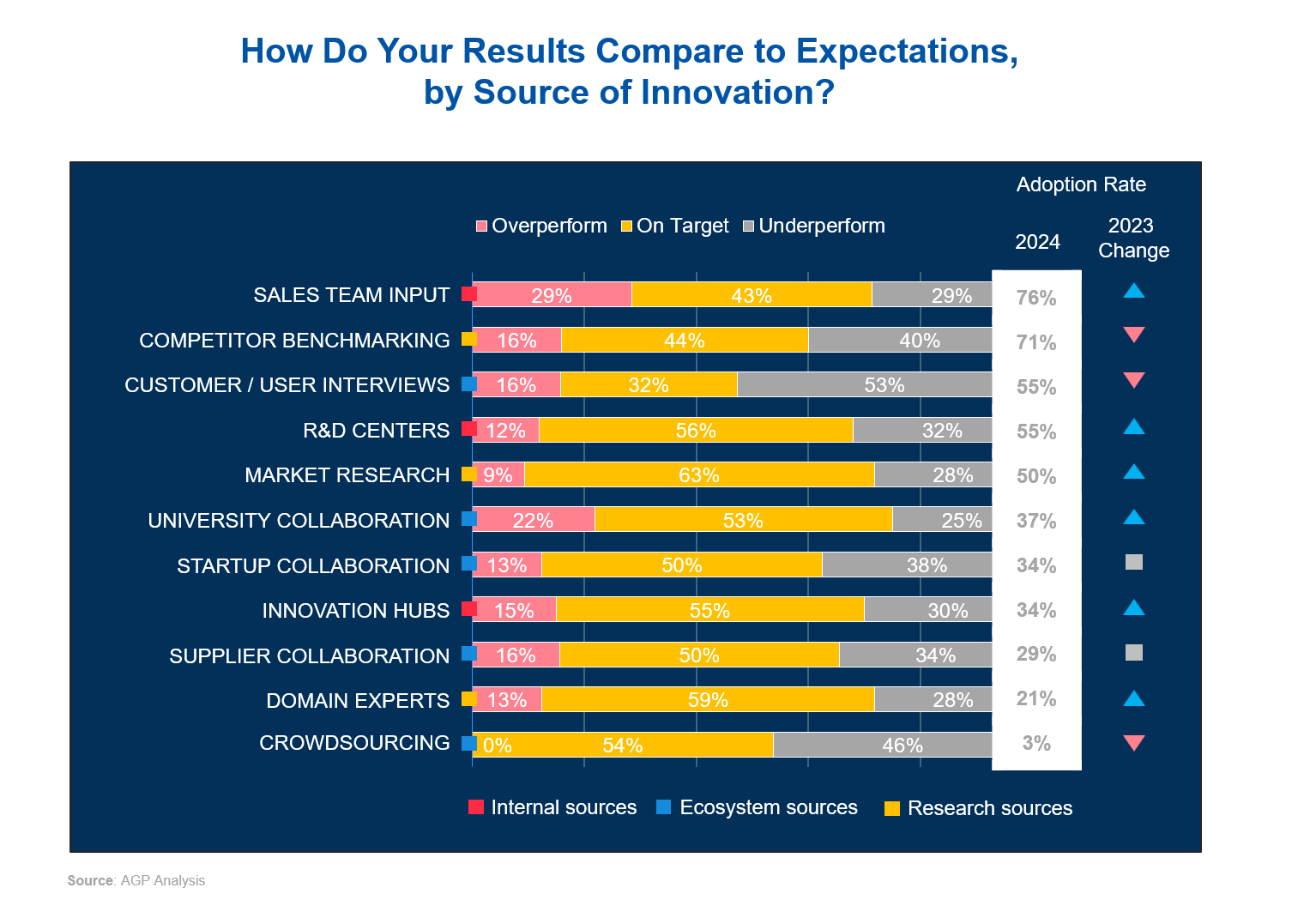
Performance of Innovation by Source of Ideas and Initiatives
Sales team input is the most commonly adopted source of innovation, with a 76% adoption rate. Beyond being extensively used, this source shows strong results, with 29% of ideas performing better than expected and another 29% performing worse.
Other popular sources of innovation include competitor benchmarking and customer/user interviews, with adoption rates of 71% and 55%, respectively. However, their performance outcomes show room for improvement. For competitor benchmarking, 16% of ideas perform better than expected, while 40% fall short. Customer/user interviews show 16% of ideas performing well, but 53% underperforming.
Grouping sources of innovation into buckets (internal, ecosystem, and research sources) reveals further performance patterns. Internal sources - sales team input, R&D centers, and innovation hubs - show an average of 19% of ideas performing better than expected and 30% performing worse.
Ecosystem sources, such as university and supplier collaborations, show mixed results. Ideas from university collaboration performed second best (22%), but ecosystem sources have an average of 13% of ideas performing well and a higher rate of 39% performing worse. This suggests that while external partnerships can provide diverse ideas, they come with challenges that can limit their effectiveness. For ecosystem collaboration to succeed, strong integration and shared goals are essential.
Overall, sources of ideas overperformed only 14% of the time, while a significant 35% underperformed. These results indicate that many innovation channels are not used to their full potential or require better oversight.
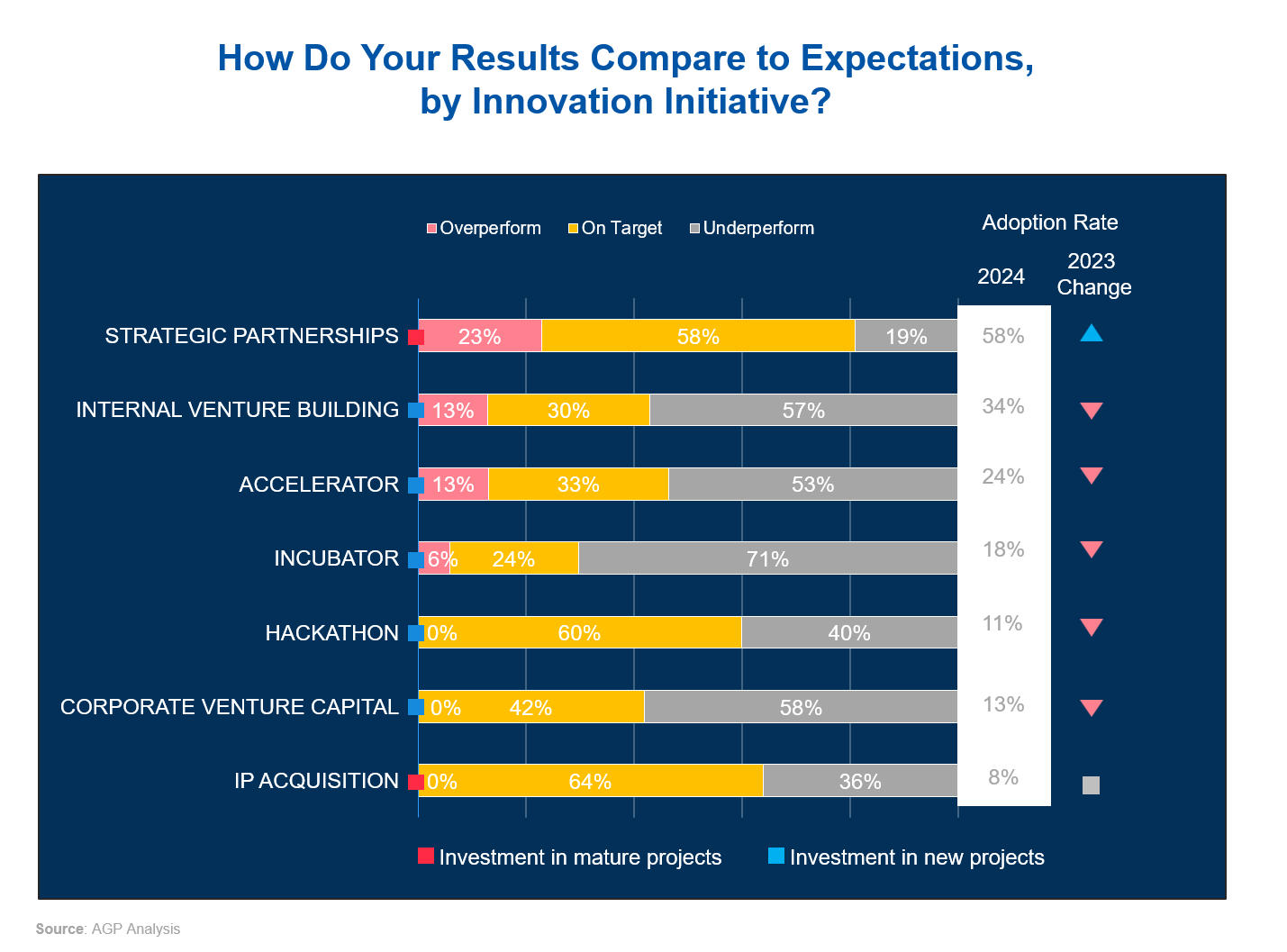
Strategic partnerships are the most successful type of innovation initiative, with 23% of them outperforming expectations and only 19% underperforming. This initiative also has the highest adoption rate at 58%. Such partnerships likely benefit from the established relationship and trust built over time, contributing to their relatively high success rate, compared to other initiatives.
Internal venture building and accelerators come next in terms of performance, each showing 13% of their initiatives exceeding expectations. However, both initiatives present challenges, as 57% and 53% of their efforts, respectively, fall short of expectations.
Incubators, with an adoption rate of 18%, show that 71% of their initiatives do not meet targets. Hackathons and corporate venture capital also show limited success, with 40% and 58% of their initiatives, respectively, underperforming.
How are companies approaching China AI adoption
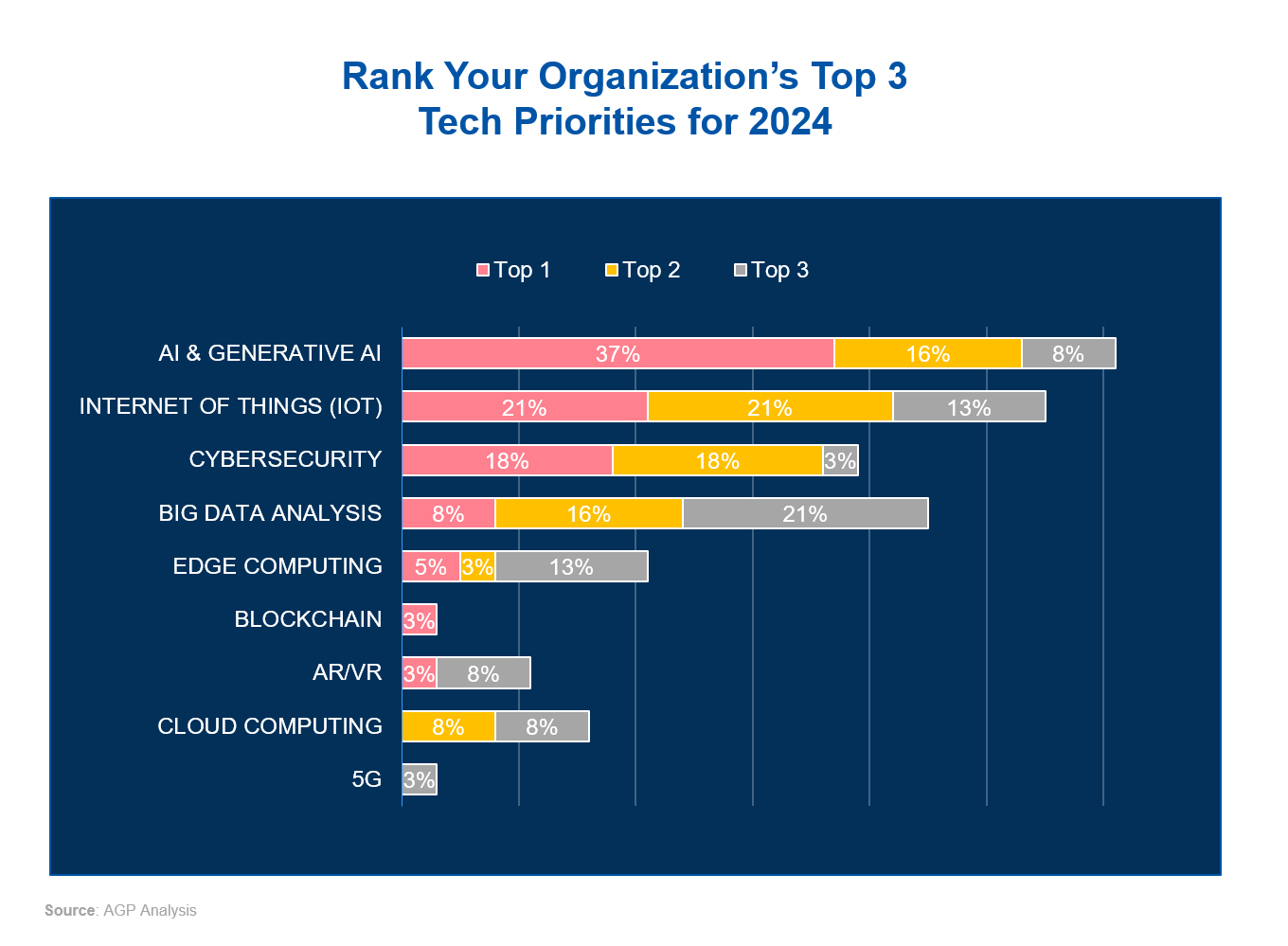
When ranking top technological priorities for 2024, MNCs identified AI and GenAI as the leading focus, with 37% of respondents ranking it as their number one priority, followed by 16% including it as a second priority, and 8% as third. This shows a clear trend towards prioritizing advancements in AI capabilities as central to business strategies.
The Internet of Things (IoT) and cybersecurity follow as the next most important technologies, with IoT selected as the top priority by 21% of respondents and cybersecurity by 18%. Both areas also feature prominently as second and third priorities, illustrating their critical roles in supporting connectivity and ensuring data protection in an increasingly complex digital landscape.
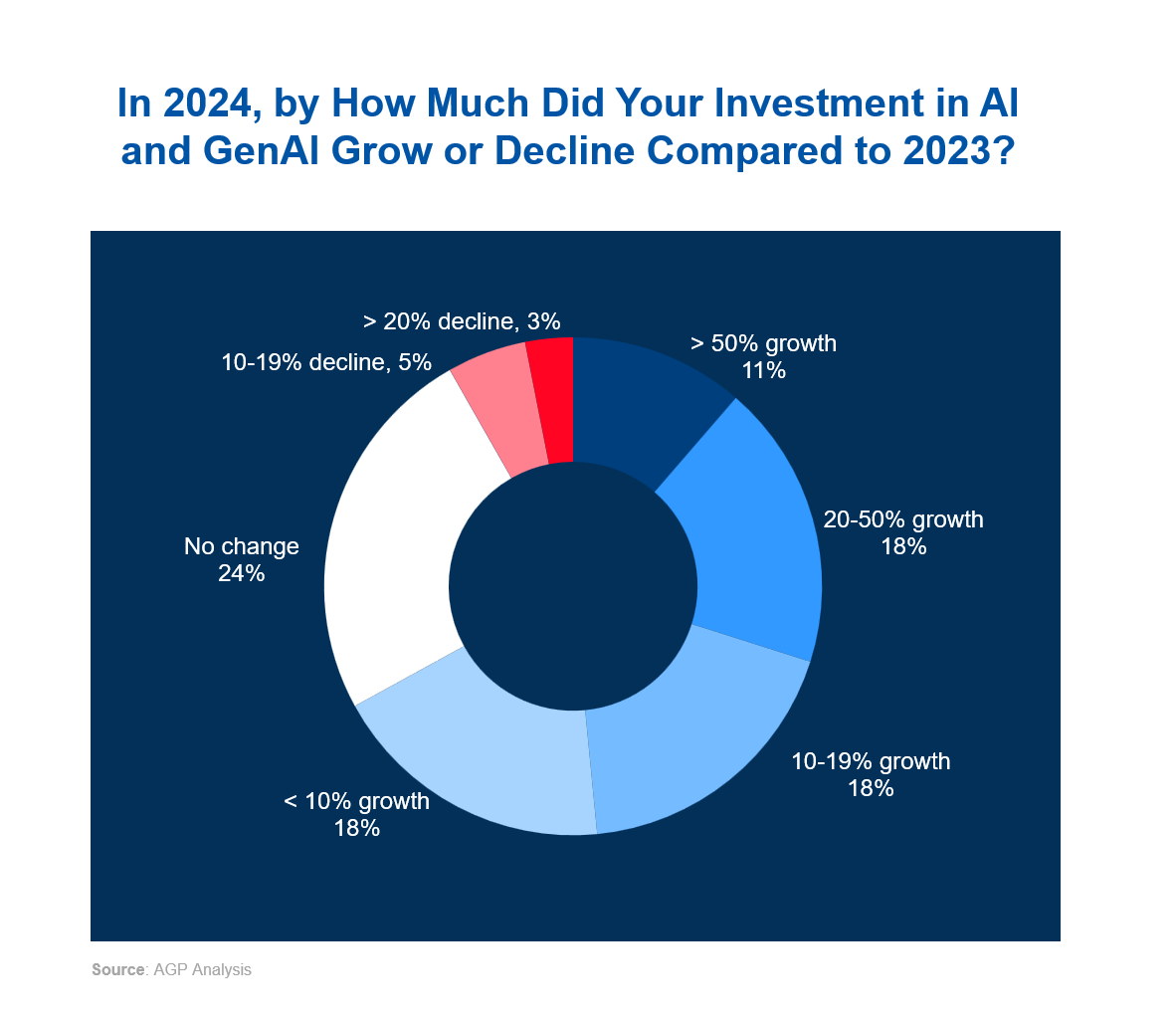
According to our research, 68 % of MNCs increased spending on AI in 2024 compared to 2023, with half growing investment by at least 10% and a notable 11% of organizations reporting an increase of over 50% in investment, indicating strong confidence in these technologies' potential. Only 8% of companies reduced investment.
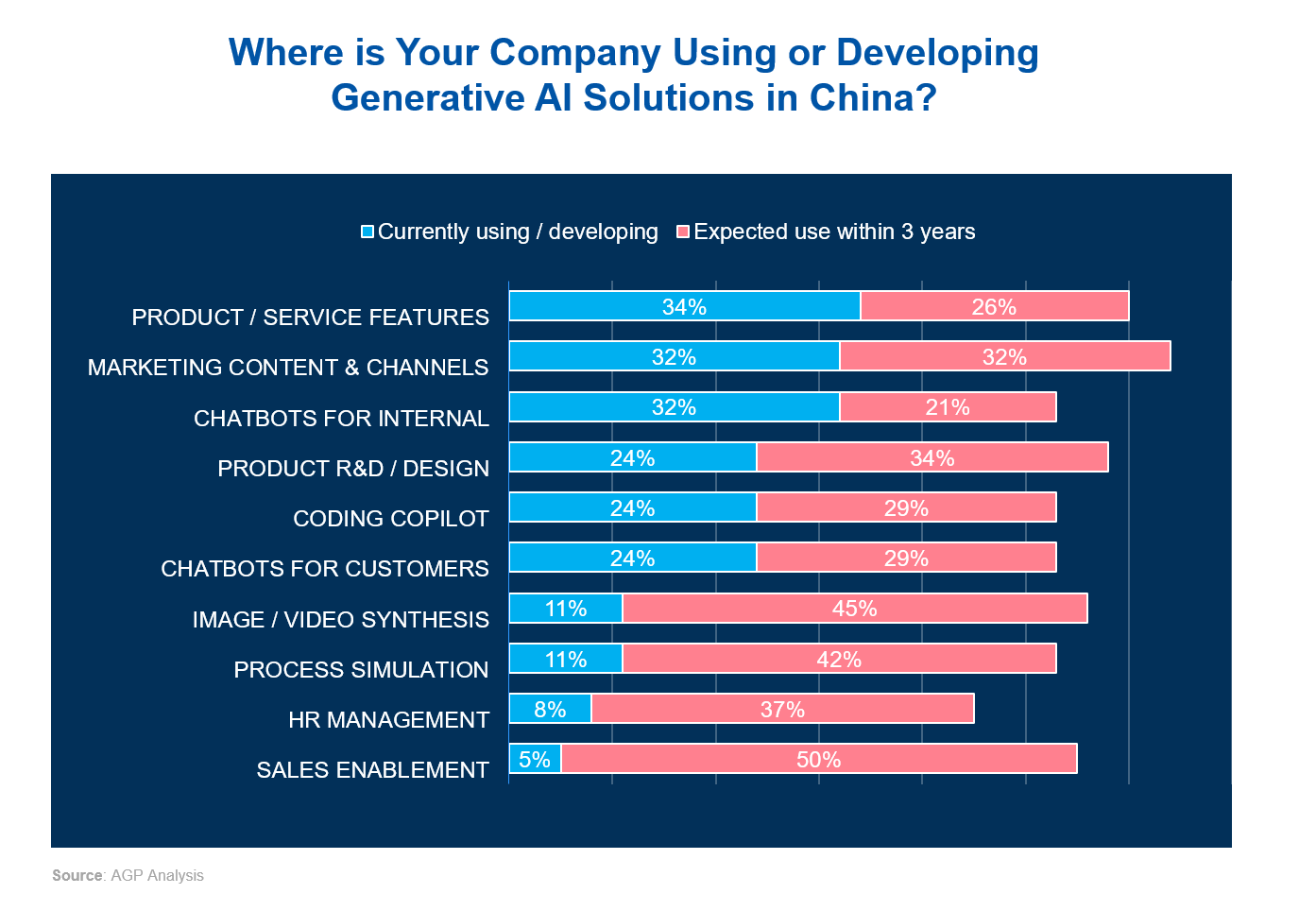
 The application of generative AI within companies in China reveals diverse use cases. On the one hand, companies are currently leveraging generative AI predominantly for enhancing products (34%), marketing (32%), and operational efficiency: chatbots for internal use (32%), product design (24%), coding Copilot (24%), and chatbots for customers (24%). On the other hand, future trends signal substantial growth in areas such as sales enablement (50%), image/video synthesis (45%), process simulation (42%), and HR management (37%). These projections suggest that as organizations grow more confident in AI’s capabilities, they will be expanding their use to more specialized and strategic areas.
The application of generative AI within companies in China reveals diverse use cases. On the one hand, companies are currently leveraging generative AI predominantly for enhancing products (34%), marketing (32%), and operational efficiency: chatbots for internal use (32%), product design (24%), coding Copilot (24%), and chatbots for customers (24%). On the other hand, future trends signal substantial growth in areas such as sales enablement (50%), image/video synthesis (45%), process simulation (42%), and HR management (37%). These projections suggest that as organizations grow more confident in AI’s capabilities, they will be expanding their use to more specialized and strategic areas.
The affordability and availability of AI tools in China’s advanced AI ecosystem, second only to the US, not only encourage companies to leverage AI for current applications such as product enhancements or marketing but also foster innovation and experimentation, allowing businesses to become more confident in their AI capabilities and, subsequently, to expand their applications.
Strategic Recommendations for MNCs
Multinational companies (MNCs) operating in China are navigating a rapidly evolving innovation landscape, driven by the country’s strong engineering capabilities, policy support, and global market influence. The findings from the 2024 "Innovating in China" benchmarking study highlight essential strategies MNCs are adopting to remain competitive and maximize their potential in this dynamic market.
Adopting a “China for China” and “China for Global” Strategy: Shifting away from traditional headquarters-led strategies to tailor innovations to the unique needs of the Chinese market is crucial. Simultaneously, embracing a “China for Global” strategy leverages China’s rapid prototyping and strong R&D ecosystem to contribute to global product development.
Address Financial and Alignment Challenges: Financial constraints and alignment between global and local leadership remain challenges for MNCs, cited by 20% and 18% of respondents, respectively. Companies must ensure proper resource allocation and promote better integration of local insights into global strategies to mitigate these challenges and improve the impact of their innovation initiatives.
Prioritize Disruptive Over Incremental Innovation: Competitive pressure in China’s market is intense, particularly in pricing and sales/service speed. Incremental improvements are no longer sufficient to maintain market share. The report indicates a significant trend towards prioritizing disruptive innovation, with the proportion of companies focusing on new product innovation expected to grow from 66% in 2024 to 71% by 2027.
Strengthen Strategic Partnerships: The report highlights strategic partnerships as the most successful type of innovation initiative, with 23% outperforming expectations. Establishing long-term partnerships that foster trust and collaboration with local firms or research institutions will enable MNCs to effectively tap into China’s innovation ecosystem in a manner proven to be more effective than other innovation initiatives.
Capitalize on China’s AI Ecosystem: AI and Generative AI are the current top tech priorities, and 68% of MNCs have increased their spending on AI in 2024. Companies are planning to expand their use of generative AI from current applications in product enhancements and marketing (34% and 32%, respectively) to other strategic uses, such as sales enablement (projected to grow to 50%), image/video synthesis (45%), and process simulation (42%). China’s AI ecosystem—second only to the US—provides MNCs with a wide array of affordable and innovative tools to further explore and develop their capabilities.
AGP Insights
Download PDF.
Your PDF report was sent successfully to your inbox!
Related Insights.











