Dassault Systemes
3D 体验公司。
概述
|
总部
法国
|
成立年份
1981
|
公司类型
上市公司
|
收入
$1-10b
|
|
员工人数
10,001 - 50,000
|
网站
|
股票行情
OTCMKTS: DASTY
|
推特句柄
|
公司介绍
3DEXPERIENCE 公司 Dassault Systèmes 为企业和个人提供虚拟世界,以想象可持续的创新。其世界领先的解决方案改变了产品的设计、生产和支持方式。达索系统的协作解决方案促进社会创新,扩大虚拟世界改善现实世界的可能性。该集团为 140 多个国家/地区的所有行业的 190,000 多名不同规模的客户带来价值。
物联网解决方案
主要客户
宝马、法国巴黎银行、猛犸象体育
物联网应用简介
Dassault Systemes 是基础设施即服务 (iaas), 平台即服务 (paas), 分析与建模, 功能应用, 和 网络与连接等工业物联网科技方面的供应商。同时致力于航天, 汽车, 化学品, 建筑与基础设施, 消费品, 电子产品, 设备与机械, 生命科学, 海洋与航运, 半导体, 电信, 运输, 和 公用事业等行业。
技术栈
Dassault Systemes的技术栈描绘了Dassault Systemes在基础设施即服务 (iaas), 平台即服务 (paas), 分析与建模, 功能应用, 和 网络与连接等物联网技术方面的实践。
-
设备层
-
边缘层
-
云层
-
应用层
-
配套技术
技术能力:
无
弱
中等
强

Supplier missing?
Start adding your own!
Register with your work email and create a new supplier profile for your business.
实例探究.

Case Study
Aerospace & Defense Case Study Airbus
For the development of its new wide-body aircraft, Airbus needed to ensure quality and consistency across all internal and external stakeholders. Airbus had many challenges including a very aggressive development schedule and the need to ramp up production quickly to satisfy their delivery commitments. The lack of communication extended design time and introduced errors that drove up costs.

Case Study
High Tech Case Study Dongyang E&P
To achieve global leadership, Dongyang E&P needed to improve collaboration between product development teams. The company already had a product lifecycle management (PLM) system in place, yet it needed a platform that would facilitate collaboration and improve problem detection before going to mass production.
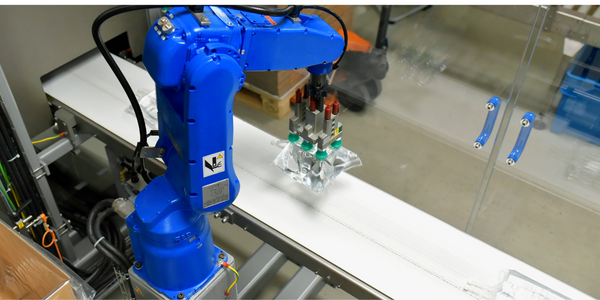
Case Study
Flow Robotics: Scaling Up Production and Accelerating Product Development with IoT
Flow Robotics, a Danish manufacturer, developed flowbot™ ONE pipetting robots to alleviate the strain on bioanalysts in life-science laboratories and hospitals across Europe. These robots were designed to automate part of the testing process, speeding up the time it takes to produce results and reducing pressure on staff. However, the company faced challenges in scaling up production and accelerating product development. High workloads and physically challenging conditions have long been an issue for laboratory professionals. Flow Robotics estimates that around half of medical lab technicians carry out the same arm movements for at least a quarter of their working day. The American Society for Clinical Pathology reported that 85% of laboratory professionals feel burnt out; 36% struggle with inadequate staffing; and 32% face a heavy workload and pressure to complete all testing on time.

Case Study
Toyo Tire's Digital Transformation: Enhancing Product Development with IoT
Toyo Tire, a Japanese-based tire manufacturer, was facing the challenge of keeping up with the rapid changes in the automotive industry. With the advent of electric vehicles and connected cars, the company recognized the need to innovate and develop new types of tires to meet these specific needs. However, their existing product development processes were not sufficient to keep pace with the industry's transformation. The company's data was held in siloes, preventing users from easily accessing all the information they needed. This lack of integration was hindering their ability to innovate and develop new products efficiently. Toyo Tire needed a solution that would accelerate its product development processes and put innovation at the core of its activities.
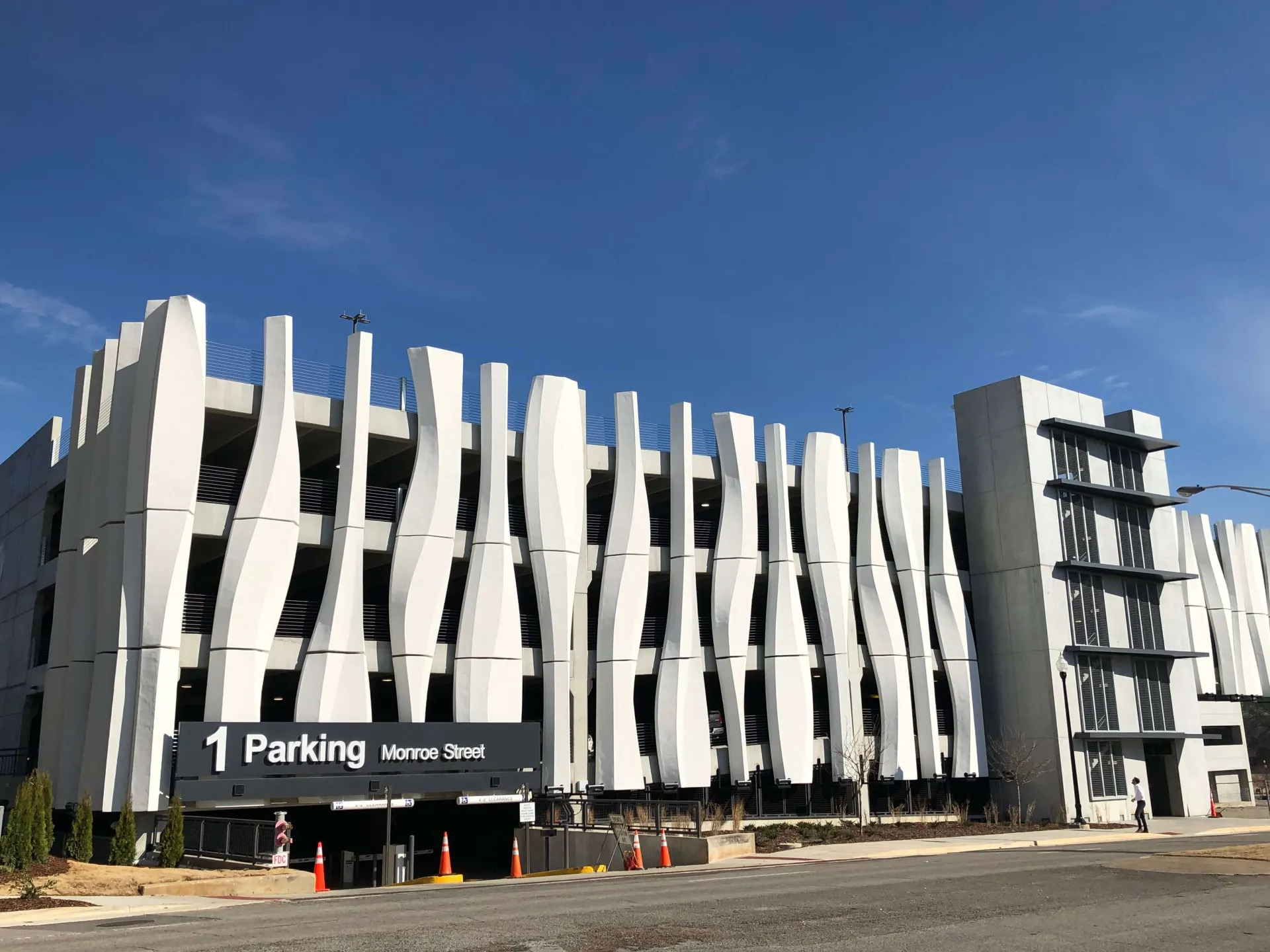

Case Study
Branch Technology: Achieving 100% Accuracy in Modeling with 3DEXPERIENCE Cloud Platform
Branch Technology, a Tennessee-based company that designs and manufactures commercial facade systems, was in need of a software solution that could process complex geometries to produce a multitude of components for various digital fabrication methods. The company was inspired by nature's efficient cellular structures and had developed a construction-scale, freeform 3D-printing technique and direct digital manufacturing approach called cellular fabrication (C-Fab®). However, they were facing challenges in implementing a digital process that could eliminate digital fabrication bottlenecks, be easily updated, and yield high fidelity parts. The company was in search of a solution that could help them imagine, compose, and construct complex design structures with ease and precision.

Case Study
ALCAN Systems: Revolutionizing Cellular and Satellite Communication with IoT
ALCAN Systems, a start-up founded in 2016, aimed to create a low-cost smart antenna system for cellular and satellite communication. The company was developing liquid-crystal-based phased-array antennas that allow high-performance electronic beam-steering in a compact, lightweight package. However, the development of these innovative antennas posed significant challenges. Traditional mobile technology used omnidirectional antennas that provided coverage from as many directions as possible. This approach was not suitable for the future of satellite broadband and millimeter-wave 5G. For these technologies to work effectively, the end-user needed a constant line of sight to the satellite, which required a very high directivity and gain to maintain contact without excessive power use. The same was true for 5G, especially at very high frequencies where loss from waves passing through the air and other materials was much higher. ALCAN Systems needed a solution that could overcome these challenges and deliver reliable high-speed data links in challenging environments.
Case Study
Global Unichip Corporation: Streamlining IC Design with IoT
Global Unichip Corporation (GUC), Taiwan’s sixth largest integrated circuit (IC) design company, faced challenges in managing its intricate supply chain. The company aimed to function as a key design hub integrating IP providers and IC design partners. However, internal processes were disjointed with departments operating in silos and unsynchronized communication between systems. Project status reports were inaccurate due to manual weekly updates. Managing product issues was resource-intensive and problem-solving knowledge was not accumulated or compiled into a database. Furthermore, GUC needed to continually communicate, coordinate, and collaborate with various business partners such as wafer manufacturers, packaging plants, and test plants after each project completion. This necessitated a comprehensive project management integration platform to handle complex internal and external business processes.

Case Study
Streamlining Product Development and Testing: Fujitsu's Journey with Dassault Systèmes
Fujitsu Network Communications, a leading optical solutions provider, faced challenges in managing customer requirements for increasingly complex products, developing solutions, and testing them on accelerating schedules. The company's document-based system made it difficult to reuse requirements and communicate them to downstream groups, necessitating a shift from a document-centric approach to a data-centric one. Managing large numbers of documents was time-consuming and lacked visibility, making it hard to keep the requirements and test teams in sync. The company was also experiencing issues with testing requirements or writing test cases for requirements that had been modified or no longer existed. Fujitsu needed a solution to eliminate these inefficiencies and streamline its processes.
Case Study
Lenovo ThinkPads Get Tougher and More Sensitive with Abaqus FEA
Lenovo's ThinkPad line of laptops is known for its aesthetics and durability. However, the challenge lies in ensuring that the laptops are not only portable but also durable. The laptops face demanding loads and forces even when they’re just being carried from place to place. It’s important for the covers to be stiff enough, with minimal deformation, so that the rear cover will protect the display, while the base cover protects the motherboard. Another challenge was to reduce the thickness of the keyboard assembly without losing the traditional keystroke feel.
Case Study
Consumer Packaged Goods and Retail Case Study - General Mills France
General Mills France, a subsidiary of a world-leading food company General Mills, wanted to increase its share of the ice cream market by expanding its Häagen-Dazs premium ice cream brand to respond to consumers’ increased inclination for snacking. The company needed to design the most efficient and innovative merchandising strategy to launch its expanded line of Häagen-Dazs ice cream. The key to success was innovative merchandising. The company engaged with major French retailers to implement the most effective way to position and merchandise its products to maximize category growth and brand revenue.
Case Study
MicroPort Life Sciences Case Study
Shanghai MicroPort Orthopedics was looking to expand into new orthopedic products. They were particularly interested in total knee replacement (TKR) implants and wanted to compare the performance of fixed-bearing and mobile-bearing designs. The company wanted to conduct its own research and development to bring out innovative products. However, traditional methods of testing prototype designs in the lab using a bench-top device called the Kansas Knee Simulator (KKS) were costly and time-consuming.
Case Study
Tetra Pak Consumer Package Goods & Retail Case Study
Tetra Pak, the world's largest supplier of aseptic packaging, was faced with the challenge of ensuring the integrity of aseptic packaging by modeling the complex fluid-structure interaction of the filling and sealing process. This included the packages, liquid, and machines. The company wanted to control the process completely, which required an in-depth knowledge of the loads and forces involved. The packaging process was designed to be as simple as possible, but this simplicity posed tremendous engineering challenges. The packaging material was very thin and flexible, which made for large deformations under pressure changes. The cross-section of the tube rapidly changed from circular cross-section to fully closed when folded. Most importantly, there was a strong fluid-structure interaction to be modeled that had to take into account the changing pressure waves in the fluid and their effects on the packaging material.
Case Study
Fast Resource Estimation Helps Improve Operational Efficiency
The mining industry is facing a challenge with the increasing size of datasets as mining companies develop and expand existing properties. The large data size has made it difficult for mining software to keep pace, often taking hours or even days for geology and mine planning applications to update models. This delay in updating models can lead to inefficiencies in production scheduling and increased costs. For instance, if waste material is sent to processing, the mining company will spend unnecessary money without a return and create unnecessary wear on equipment, shortening its life cycle and driving up maintenance costs.
Case Study
Industrial Equipment Case Study: Doosan Infracore
Doosan Infracore, a globally renowned player in the industrial equipment industry, aimed to become one of the top three global machinery suppliers by 2020. To achieve this, the company needed to improve the productivity and product quality of its 14 subsidiaries and R&D centers in the US, China, Norway, and the Czech Republic. The company faced challenges in reducing product development time, errors, and rework, and improving data integration and security throughout the product lifecycle. Their existing PLM system, a collection of heterogeneous, tailor-made, in-house software applications, generated data incompatibility issues from one site to another, making it difficult to address these challenges.
Case Study
DS PLM SUCCESS STORY - Panasonic Home Appliances
Panasonic Home Appliances, a specialist in household appliances, faced a challenge of reducing product development lead time dramatically. The company needed to transition from 2D drawings to 3D design to meet the increasing demand for induction heated (IH) ranges and other IH-at-able cooking appliances. The spike in demand for IH ranges beginning around 2000 and new competitors quickly hitting the market, Panasonic knew it needed to adopt Product Lifecycle Management (PLM) technology quickly. With its customers demanding greater product variation, Panasonic understood that to remain competitive it must demonstrate consistent improvement in the functionality and quality of its products. Panasonic also knew that it must reduce costs and shorten development lead-time.
Case Study
WITTUR Industrial Equipment case study
Wittur, a leading manufacturer of elevator components, modules and systems, faced a challenge following a series of acquisitions. The company needed to leverage the massive amount of diverse data across its globally-located plants and to increase part reuse. As it acquired companies and established production plants and sales organizations around the world, Wittur found itself faced with a diverse IT environment that prevented its employees from easily finding and leveraging all of its information. Data was stored in different legacy SQL databases each with their own material codes, norms and structure, which had to be sifted through individually. This was extremely time-consuming. Another challenge was to reduce the number of duplicate parts in its system. The engineers were having difficulty finding existing parts for new projects, so they preferred redesigning them, even though, in many cases, a similar part existed. This continuous duplication of parts required additional storage space. It also drove up costs as redesigning a part includes R&D, manufacturing, testing, logistics and inventory, all activities that could be avoided if they could just find an existing part to fit the bill.
Case Study
Academia Case Study: Chitkara University
Chitkara University in Chandigarh, India, was faced with the challenge of providing its students with a multi-disciplinary education while encouraging initiative and entrepreneurship through projects and contests based learning. The university wanted to increase the employability of its students and enable them to design products that bring value to society. The university also wanted to help Indian companies gain a competitive advantage in the global marketplace by producing students proficient in technologies used globally. The university's student-centric approach and focus on innovation and entrepreneurship required a platform that could support these objectives.
Case Study
Enquip Improves manufacturing performance by 30% with CATIA and ENOVIA
Enquip, a Brazilian company that develops and manufactures industrial equipment for use in cargo handling solutions, was seeking to optimize its manufacturing processes and make better use of its existing hardware and machines. The company faced a key challenge in expanding and improving the management of its engineering data, a function that was previously limited due to integration and programming issues with production equipment. Enquip required an integrated PLM solution that was both robust, came with technical support, and was easy to integrate into existing software solutions.
Case Study
NSE Composites: Energy, Process and Utilities Case Study
NSE Composites was tasked with analyzing loads, stresses, and fatigue for an innovative, sweep-twist wind turbine blade design that is targeted to capture significantly more energy on light-windspeed sites. The basic physics and economics of wind turbine blades are relatively simple. Their power output is roughly proportional to the square of blade length. This relationship pushes designers to create increasingly longer blades for harvesting additional kilowatts. Secondly, as blades get longer, weight increases—by approximately the cube of the length—leading to higher raw material costs. This correlation sends designers in search of weight-efficient geometries that are strong and rigid enough to weather the increased loading inherent in longer blades.
Case Study
Tyco Fire Protection Products High Tech Case Study
Tyco Fire Protection Products needed to provide its new production factory in the Czech Republic with easy access to up-to-date design information. The factory was not originally part of Tyco, but belonged to a manufacturing company producing electronic products for various customers including Tyco. After the factory was purchased by Tyco, it needed to transition from its older ENOVIA MatrixOne system to Tyco’s ENOVIA Version 6 application, part of the 3DEXPERIENCE Platform from Dassault Systèmes. The transition had to be done quickly as Tyco management announced that MatrixOne would no longer be accessible after three months.
Case Study
Ds Plm Success Story - Zvezda
Zvezda, a leading Russian toymaker, faced challenges in maintaining its lead in the domestic market and securing its entry into the international market. The company needed to reduce product development time and modernize its operations with state-of-the-art technology used in modern toy manufacturing. The company's traditional methods based on outdated drawing technology were insufficient for creating exact replicas of modern aircraft, which have exceptionally sophisticated interior layouts. Increased competition in domestic and international toy markets forced Zvezda to adopt a new strategy that ensures technological support of its production process. The company's main business goals, such as constantly replenishing its stock, improving product quality, and focusing on innovation, necessitated the implementation of a more powerful system for automated design.
Case Study
Maschio Gaspardo Case Study
Maschio Gaspardo, an Italian agricultural equipment manufacturer, was facing the challenge of meeting the diverse needs of farmers across the globe. The company needed to implement a flexible business environment to rapidly develop a full range of products tailored to farmers’ diverse needs. The demand for customized equipment and services was increasing due to varying local farming needs such as size of land or soil composition. Moreover, the growing demand for organic food and sustainable farming methods had changed the way the land is cultivated. The company's customers expected them to provide precision farming solutions through innovative equipment delivered fast without compromising on quality. To meet these challenges, Maschio Gaspardo needed to transform its business and improve collaboration among design, sourcing, production, and service teams.
Case Study
West Virginia University Uses SIMULIA for Inflatable Tunnel Plug Development
West Virginia University (WVU) was tasked by U.S. Homeland Security to develop large inflatable plugs for use in emergency situations requiring the closing of vehicular tunnels or other large cylindrical structures. The challenge was that refining prototypes in a test facility was complex and time-intensive. The need for such a plug was driven by incidents such as the flooding of New York City’s subways during Hurricane Sandy, a truck fire in the Mont Blanc Tunnel, and the release of sarin gas in the Tokyo subway system. The idea was to set up inflatable structures, either permanently or temporarily, in multiple locations where an emergency was anticipated.
Case Study
Pol-Eko-Aparatura Reduces development time by 50% with CATIA PLM Express
Pol-Eko-Aparatura, a leading Polish producer of laboratory equipment, was facing the challenge of meeting the demands of its growing customer base without increasing cost or compromising quality. The company was operating in a highly specialized laboratory equipment market, facing stiff competition from neighboring Germany. While lower product costs due to lower Polish wages gave Pol-Eko-Aparatura a competitive advantage over its German rivals, it was not enough to guarantee success. Therefore, the company focused on reducing time-to-market while maintaining high standards of design quality. The company was using a third-party CAD system, which was not efficient enough to meet their needs.
Case Study
DS PLM SUCCESS STORY - TÜV SÜD: Certifying nuclear power plants with Abaqus FEA from SIMULIA
TÜV SÜD, a leading global technical service corporation in Filderstadt, Germany, is responsible for independently testing, inspecting, and certifying nuclear facilities for licensing by the German government. The company needed to ensure the safety of nuclear plant reactors by identifying and correcting problems that threaten the longevity of the plants. The systems, structures, and components of nuclear plants can change with time and use. Components can wear out, corrode, or degrade; instrument and control systems may become obsolete as technologies evolve. The properties of critical materials may change through heat and neutron irradiation. Identifying and correcting longevity issues can extend the operating license of a plant by several decades, which is why upgrading older facilities is a major focus of nuclear regulatory bodies and plant operators.
Case Study
Aerospace and Defense Case Study: Messier-Bugatti-Dowty
Messier-Bugatti-Dowty, a global leader in aircraft landing and braking systems, faced the challenge of finding customized solutions for each client as rapidly as possible, often across continents. The company operates in a cross-cultural, multi-site environment with technicians and engineers working in different countries who do not necessarily speak the same language and who, in the past, were using different methods and tools. Each of their sites in Gloucester (UK), Montreal and Toronto (Canada), and Bidos (France) had their own industrialization processes and tools, making data exchange difficult and collaboration practically non-existent. The company launched a Manufacturing and Engineering Data System (MEDS) project to streamline development processes by rationalizing information systems at landing gear production sites.
Case Study
DS PLM SUCCESS STORY - KT&G: Responding to market needs faster with ENOVIA
KT&G, a leading tobacco manufacturer in South Korea, was facing challenges in managing and sharing product data across its different offices. The company's brand planning team is based in Seoul, the R&D team and production factory are in Daejeon, and the packaging facility is in Chonan. The development of new products involved many steps, each requiring coordination between these different locations and management of massive amounts of information and product data. Without an effective data management system, managing and sharing the right data was a serious challenge. The company needed to implement improvements to its development process in order to effectively manage product information and its flow from one location to another.
Case Study
High-Tech case study INNODESIGN
INNODESIGN, a top ten design firm in the world, was facing a challenge in accelerating its creation of innovative products to satisfy rapidly changing consumer tastes. The company needed to improve the sharing of design ideas and streamline its design processes. The company's CEO, Youngse Kim, believed that new ideas and speedy design processes were the most important factors that contribute to a product’s victory or failure in any market. He wanted to provide Korean startups with a place they could go to obtain design expertise and financial assistance, if needed, to get their projects off the ground when starting their own businesses.
Case Study
A. Zahner Company: Pushing the Boundaries of Architecture with 3DEXPERIENCE
A. Zahner Company, a US-based architectural engineering, manufacturing, and construction firm, was facing challenges in designing more complex geometries and improving communication between project stakeholders. The company was at the forefront of a shift in architecture to digital construction, using Building Information Modeling and digital definition to improve transparency and reduce errors. However, the iterative process of architectural projects often led to communication issues between different groups. The company needed a solution that would allow for efficient collaboration and communication, as well as the ability to design complex geometries.
Case Study
No Two Hips are Alike: Mobelife leverages realistic simulation for patient-specific design and analysis of hip
The article discusses the challenges faced in hip replacement surgeries, particularly in cases where the patient has outlived the lifespan of the hip prosthesis, which is typically between 15 to 20 years. When a prosthesis fails, a revision surgery is carried out to replace the components. However, a significant challenge faced during implant revision surgery is that the pelvic bone stock is often significantly reduced. Ten-year failure rates of primary hip replacements are estimated at 11.4%. This number more than doubles to 25.6% in case of revisions. In over 58% of those revision failures, the acetabular component is involved. To deal with these challenges, a custom approach is most suitable.
Case Study
Simplifying product illustration with 3DVIA Composer from IBM and Dassault Systèmes
KaVo, a leading provider of dental equipment, was seeking to enhance the detail and usefulness of its product assembly and technical documents. The company was using 3D CATIA models to create assembly drawings, which were then converted to PDF files for use by production workers. However, the information on the PDFs was not detailed enough to ensure high-quality assembly. KaVo needed an automated solution for producing 3D interactive work instructions and product illustrations to provide the level of detail required for accurate product assembly and technical documentation. This would help to reduce the time to market.
Case Study
Dassault Aviation: Aerospace & Defense Case Study
Dassault Aviation’s Falcon Spare Parts department needed to provide a consolidated view of all spare parts information worldwide. The division was managing a global network of more than 80,000 spare parts which required precise logistical coordination. Over the years, each site has come to rely on its different solutions to locate the appropriate spare parts but, as a company, they did not have an overall and global view of their data. Moreover, these different solutions use different technologies – mainframe-based or client-server – which contributed to the isolation of each of their sites. To gain in efficiency, they needed a consolidated view of all their spare parts from any of their locations.
Case Study
Nabtesco Corporation Industrial Equipment Case Study
Nabtesco Corporation, a Japanese company known for its unique technology in robotic reduction gears, faced a challenge when expanding into energy harvesting equipment such as wind turbines and solar energy collector trackers. The company needed to ensure sufficient gear strength and long-term endurance in gusty conditions for their wind turbines. The yaw and pitch drives in a wind turbine engage with a pinion gear, which transmits power from the drive to the nacelle or blade. The rotation angle between drive and pinion gear teeth is particularly small, so repeated contact over time, particularly under the stresses of high winds and tower vibration, has the potential to damage tooth surfaces and cause assembly breakdowns. The engineers at Nabtesco needed to balance the contact between ring and pinion teeth to reduce the 'normal' stress of rotation and the sheer stress of the teeth against each other. Decreasing the stress on teeth improves their durability and that of the entire assembly as well.
Case Study
Plastic Technologies, Inc.: Leveraging Simulation for Lightweighting and Root-Cause Analysis
Plastic Technologies Inc. (PTI), a leader in plastic package design services, was seeking a more cost-effective and efficient alternative to extensive physical prototyping and testing. The company wanted to help its customers lightweight plastic container designs and aid in root-cause analysis of product failures. The focus was on designing lighter-weight versions of current packaging to reduce costs and meet consumers’ demand for more sustainable products. However, achieving the optimal design that can offset lightweight material composition with a structure that still meets stringent performance requirements was a challenge.
Case Study
DS PLM SUCCESS STORY - Arburg: Facilitating collaboration and reducing costs with CATIA, ENOVIA, and 3DVIA Composer
Arburg, a leading manufacturer of injection molding machines, faced the challenge of bringing its products to market faster, while increasing quality and lowering costs. The company's product range and the modular design of its machines placed high demands on IT services. Under the motto “securing the future with process optimization using standard IT solutions”, Arburg's CIO and his IT team worked closely with the operations departments to radically rethink the company’s IT infrastructure. The goal was to build a process-oriented IT infrastructure with virtual product management to improve time to market and increase development-to-delivery speed two-fold.
Case Study
Empowering Tomorrow’s Workforce with 3DEXPERIENCE
The challenge was to compress the development of a system of work for an Unmanned Aerial System (UAS) down to 90 days while providing the students of Wichita State University (WSU) a greater experience using real-life industry tools. The goal was to expose students to industry-related projects that provide them with learning that is not traditionally found in a textbook. The university aimed to be a model for applied learning and an economic driver for the community – where students can transition back and forth between the academic world and industry to work on real-world projects while they’re in school. The first fully collaborative project at the 3DEXPERIENCE Center is an unmanned aerial system (UAS), or drone, designed to handle multiple missions including search and rescue. The UAS was entirely designed and manufactured using Dassault Systèmes’ 3DEXPERIENCE platform and its Aerospace & Defense industry solutions.
Case Study
Consumer Goods & Retail Case Study - Mammut Sports Group
Mammut Sports Group, a Swiss mountain sports specialist and producer of alpine equipment and apparel, was facing challenges in accelerating their product innovation and managing their product information in compliance with norms and environmental regulations. The company was managing a highly diverse product portfolio and was using numerous Excel files to manage all their stock keeping units (SKU), which was time consuming and error-prone. The process of juggling between so many files eventually became complicated and information was hard to find. The company decided to consolidate all their product information in one unique system to improve coordination and to have better visibility within their product catalogue.
Case Study
DS PLM SUCCESS STORY Clip-Lok International Ltd. Danish box maker packs a punch with CATIA PLM Express
Clip-Lok International, a Copenhagen-based manufacturer of reusable, flat-packable wooden boxes, needed to secure its competitive edge by custom designing boxes that are cost effective, match the precise size and shape of their contents, and can be flattened for return shipment. The boxes are custom-made, posing many design challenges for the engineers. They had to design a box that has the optimum shape and size with respect to the products to be packaged, that is cost efficient to produce, assemble and flatten and that occupies as little space as possible during return shipment. These design challenges were met thanks to CATIA PLM Express.
Case Study
Efficient Dump Design Saves Agnico Eagle $1.4 Million
Agnico Eagle’s Meadowbank gold mine in northern Canada was facing a challenge of integrating mine design and production schedules with geological modeling to increase in-house knowledge and ensure profitability. They were struggling with a competitive software solution for over a year and needed a more efficient and effective solution. The mine is Agnico eagle’s largest gold producer, with 1.8 million ounces of gold in proven and probable reserves since the open pit began in early 2010. The mine is one of the most complicated waste management sites in Canada with 14 dikes, 9 pits, multiple dumps and more than 100 haul routes. The mine was also looking to reduce production costs and needed to modify the long-range plans on-the-go ensuring they are up to date with current operations.
Case Study
Korsö Båt sets sail with 3DEXPERIENCE technology
Korsö Båt, a family-run boatbuilding company, wanted to leverage its extensive boatbuilding knowledge and expertise with the proper software tools. The company faced stiff competition and its biggest challenge was to combine utility and good looks as every customer wanted to have the best boat. The company relied on its extensive knowledge and experience gained through years of designing boats. However, it needed a technology solution that could help it meet customer demands and stay ahead of the competition.
Case Study
Artificial Turf Gains Ground with Realistic Simulation
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association (FIFA) has set detailed regulations about the materials, substructure, installation, testing, and certification of artificial turf for playing fields. This means that turf manufacturers have to consider a multitude of factors when designing their products for performance and safety. These factors include the make-up of the individual blades to mimic the look and playing-feel of natural grass, the type of yarn/fiber to use, the shape of the fiber, its height above the field surface, its density per square meter, stiffness and dissipative behavior. All these factors affect wear, safety, and playing characteristics. Furthermore, what’s below the visible surface of the grass is just as critical. The fiber travels down through infill made of rubber or thermoplastic granulate, which provides shock absorption, controls rebound and prevents skin damage caused by sliding. Beneath that are additional layers of rubber and sand and, finally, the backing in which the grass blade is imbedded.
Case Study
Renault drives the customer experience with Version 6
Renault, a global automotive company, was seeking an enterprise-wide PLM solution that would effectively address issues of standardization for its processes and design tools. With more than 40% of its engineers located outside of France in “technocentres” in Romania, India, Korea, South America and Spain, the company needed a global engineering tool that would allow its designers to effectively and efficiently collaborate around the globe. Renault also sought a solution that would allow it to easily access and manage all of the company’s data – from product design and process to simulation, testing and resources information – while ensuring its traceability. The company wanted a single PDM that could be deployed worldwide to cover all of Renault’s needs for data management across product, process, simulation and performance.
Case Study
Superheat: Accelerating Heat-Treatment Quality Package Development with DraftSight Professional
Superheat, a leading innovative heat-treatment provider, was facing challenges in handling DWG files received from customers and accelerating heat treatment package development. The company was using SmartDraw 2D software for creating layouts for its heat-treatment quality packages and SOLIDWORKS® 3D design software for developing more specialized and sophisticated heat-treatment designs. However, the 2D software had limited capabilities and could not read DWG files, the most common customer format for components requiring heat treatment. It also had difficulties in manipulating engineering drawing layers. This situation prompted Superheat to look for other 2D design solutions that could improve efficiency and accelerate the development of heat treatment packages.
Case Study
Innovative Manufacturing Services: Enhancing Conveyor System Development with DraftSight Professional
Innovative Manufacturing Services, Inc. (IMS) was in need of a more efficient and cost-effective 2D design solution for developing electrical schematics and accessing legacy 2D files. The company had been using SOLIDWORKS 3D mechanical design software for creating custom manufacturing and automation systems, but continued to use AutoCAD 2D software for accessing legacy design files and creating electrical panel schematics. The challenge was to find a solution that could seamlessly integrate with their existing SOLIDWORKS implementation, provide access to legacy 2D data, and support the development of electrical schematics in a more cost-effective manner.
Case Study
Accelerating Centrifuge Quoting, Sales, and Development Processes with DraftSight Professional
CentraSep Technologies, a leading manufacturer of industrial centrifuges, separation and filtration systems, environmental products, and fluid management services, was facing a challenge with its 2D drawing solution. The company had been using AutoCAD software for creating DWG files to support the drawing needs of sales, engineering, manufacturing, and documentation functions. However, the company's installed seats of AutoCAD were getting out-of-date and Autodesk no longer offers perpetual software upgrades, only more costly monthly leasing. This led CentraSep to start looking for a more cost-effective 2D solution. The company needed a solution that was easy to learn and use, worked well alongside SOLIDWORKS 3D design software, and provided a more cost-effective 2D solution.
Case Study
Cost-Effective Custom Wire Cage Product Development with DraftSight Professional
California Wire Products Corporation (Cal-Wire), a leading manufacturer of woven wire products, was facing challenges in creating custom product designs in 2D during the configuration of SOLIDWORKS 3D/ DriveWORKS automated design application. The company was using AutoCAD 2D design software, which was not only costly but also presented data compatibility issues. The company had attempted to use Autodesk Inventor 3D design software to automate development but hit a roadblock in the process. The need for a cost-effective, efficient 2D design solution was paramount, especially as the SOLIDWORKS/DriveWorks automation package was being built and configured. The company was also facing issues with opening files and losing dimensions and text blocks on drawings due to outdated AutoCAD licenses.
Case Study
Leveraging DraftSight Professional for Cost-Effective Interior Design at Haenen Design Studios
Haenen Design Studios, a brand identity and interior design consultancy based in Culver City, CA, faced a significant challenge in creating to-scale, dimensionally accurate 2D drawings of interior design concepts. These drawings were crucial for incorporating design elements and communicating interior design concepts to clients and contractors. The company's principal designer, Christine Haenen, had experience with AutoCAD® 2D design software from her student days. However, upon founding Haenen Design Studios, she found that a commercial license for AutoCAD was prohibitively expensive. She needed a more affordable 2D design and drawing package that could meet her needs without compromising on quality or functionality.
Case Study
Efficient Structural Steel Fabrication Designs with DraftSight Professional Software: A Case Study of Bill’s Custom Fab, Inc.
Bill’s Custom Fab, Inc., a family-owned business providing custom design and fabrication services for structural steel components since 1990, faced a challenge in supporting the 2D design requirements of their business more efficiently. The firm uses 2D CAD for fabricating structural steel for a variety of applications, including construction, handrails, and stair stringers. The management team, committed to quality improvements, periodically re-evaluates its design and fabrication tools to increase efficiency, boost productivity, or add capabilities. However, licensing changes with their former CAD provider led Bill’s Custom Fab to re-evaluate its 2D design solution. The firm needed a solution that was not only functional and provided a good return on investment, but also stable, compatible with major CAD formats, and capable of running LISP macros and routines, which the firm uses to create common structural steel features.
Case Study
Improving Material Handling Machinery Development with DraftSight Enterprise: A Case Study on Young Industries, Inc.
Young Industries, Inc., a manufacturer of custom-designed equipment for handling dry bulk materials, was seeking to optimize the use of 2D and 3D design tools to boost productivity and advance the development of custom material-handling systems. The company had been using the SOLIDWORKS® 3D applications platform for the past two decades, but still had needs that were better addressed with 2D tools. They had been using MountainTop® 2D design software, but decided to seek a new 2D design solution after encountering both hardware and software failures. The company needed a solution that was easier to maintain and support, included the features they needed at a better price, and was compatible with their existing SOLIDWORKS design environment.
Case Study
Innovative Yacht Designing with DraftSight: A Case Study of GPNA S.R.L.
Griscia Pastacaldi, a former technical officer with the Italian navy and a talented naval architect designer and mechanical engineer, founded GPNA S.R.L. in 2018. The firm focuses on creating innovative yacht designs for a variety of clients, emphasizing high-quality designs and top-notch technical support. However, Pastacaldi faced challenges with the design tools he had previously used at other naval architecture design firms. He found AutoCAD® and MicroStation® 2D design software increasingly complex and less intuitive, with too many commands that took up too much space from the working area. This led him to investigate other solutions that would be more efficient and cost-effective for his new firm.
Case Study
Revamping Custom Cabinetry Design with DraftSight Professional
MAC Design and Build, a family-owned contracting business, specializes in creating custom cabinetry, furniture, doors, and built-ins for home and business furnishing and remodeling services. The company prides itself on delivering unique interior design and remodeling services that are only limited by the client's imagination and budget. However, the company faced a significant challenge in accelerating the development of these custom pieces while simultaneously eliminating errors and reducing costs. The company initially used AutoCAD 2D design software for designing the cabinets and woodworks, which are at the core of the firm's business. However, the annual licensing costs of AutoCAD, roughly $1,200 for two seats, were too high for the company. They needed a more cost-effective 2D solution that could deliver the same capabilities as AutoCAD.
同类供应商.
---nyse--ge_1.jpg)
Supplier
General Electric
GE is a diversified specialty equipment, infrastructure and financial services company. Their products and services range from aircraft engines, power generation, oil and gas production equipment, and household appliances to medical imaging, business and consumer financing and industrial products. GE believes new technologies will merges big iron with big data to create brilliant machines. This convergence of machine and intelligent data is known as the Industrial Internet, and it's changing the way we work. Year founded: 1892 Revenue: $148.5 billion (2014) NYSE: GE Featured Subsidiaries/ Business Units: - GE Digital - GE Predix - GE Intelligent Platform - Wurldtech

Supplier
PTC
PTC is a global provider of technology platforms and solutions that transform how companies create, operate, and service the "things" in the Internet of Things (IoT). The company's next-generation ThingWorx technology platform gives developers the tools they need to capture, analyze, and capitalize on the vast amounts of data being generated by smart, connected products and systems. The company's field-proven solutions are deployed in more than 26,000 businesses worldwide to generate a product or service advantage. PTC's award-winning CEO, considered an industry thought leader, co-authored the definitive guides to the impact of the IoT on business in the Harvard Business Review.

Supplier
Altair
Altair is a leading provider of enterprise-class engineering software enabling innovation, reduced development times, and lower costs through the entire product lifecycle from concept design to in-service operation. Our simulation-driven approach to innovation is powered by our integrated suite of software which optimizes design performance across multiple disciplines encompassing structures, motion, fluids, thermal management, electromagnetics, system modeling and embedded systems, while also providing data analytics and true-to-life visualization and rendering.
_1.jpg)
Supplier
Bosch
Bosch is an industry leader in automobile and industrial equipment, as well as consumer goods and building systems. Bosch operates via 440 subsidiaries in 60 countries; its core lines include mobility (auto) systems, from diesel/hybrid drive to steering, starter motors and generators, electronics, and brakes.Year founded: 1886Revenue: $58.7 billion (2014)Portfolio Companies:- Bosch Software Innovations- Rexroth- Deepfield Robotics- Escrypt- ProSyst

Supplier
ESI Group
Founded in 1973, ESI Group envisions a world where Industry commits to bold outcomes, addressing high stakes concerns - environmental impact, safety & comfort for consumers and workers, adaptable and sustainable business models. ESI is present in more than 20 countries, employs 1200 people around the world and reported 2020 sales of €132.6 million. ESI is headquartered in France and is listed on compartment B of Euronext Paris.







